109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

脂质包覆的中空介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子用于递送 miR-375 和盐酸多柔比星 (doxorubicin),以克服肝细胞癌中的多重耐药性
Authors Xue H, Yu Z, Liu Y, Yuan W, Yang T, You J, He X, Lee RJ, Li L, Xu C
Received 22 February 2017
Accepted for publication 18 April 2017
Published 24 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5271—5287
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S135306
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Yang Liu
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
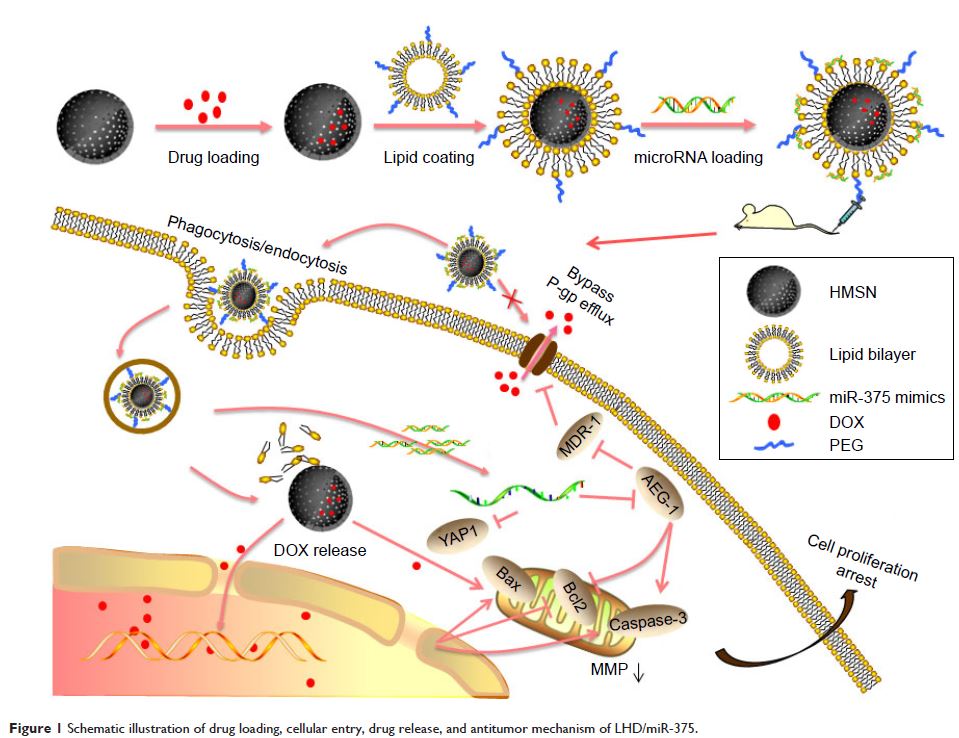
Abstract: Multidrug resistance (MDR) due to overexpression of P-glycoprotein
(P-gp) is a major obstacle that hinders the treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC). It has been shown that miR-375 inhibits P-gp expression via inhibition
of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) expression in HCC, and induces apoptosis
in HCC cells by targeting AEG-1 and YAP1. In this study, we prepared
lipid-coated hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (LH) containing doxorubicin
hydrochloride (DOX) and miR-375 (LHD/miR-375) to deliver the two agents into
MDR HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. We found that LHD/miR-375 overcame drug
efflux and delivered miR-375 and DOX into MDR HepG2/ADR cells or HCC tissues.
MiR-375 delivered by LHD/miR-375 was taken up through phagocytosis and
clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Following release from late
endosomes, it repressed the expression of P-gp in HepG2/ADR cells. The
synergistic effects of miR-375 and hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles
(HMSN) resulted in a profound increase in the uptake of DOX by the HCC cells
and prevented HCC cell growth. Enhanced antitumor effects of LHD/miR-375 were
also validated in HCC xenografts and primary tumors; however, no significant
toxicity was observed. Mechanistic studies also revealed that miR-375 and DOX
exerted a synergistic antitumor effect by promoting apoptosis. Our study
illustrates that delivery of miR-375 using HMSN is a feasible approach to
circumvent MDR in the management of HCC. It, therefore, merits further
development for potential clinical application.
Keywords: hollow
mesoporous silica nanoparticle, doxorubicin, miR-375, AEG-1, hepatocellular
carcinoma, multidrug resistance