109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Foxj2 过表达与鼻咽癌的不良预后、发展和转移相关
Authors Shan Y, Chang T, Shi S, Tang M, Bao L, Li L, You B, You Y
Received 16 February 2017
Accepted for publication 19 April 2017
Published 24 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3733—3741
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S134915
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
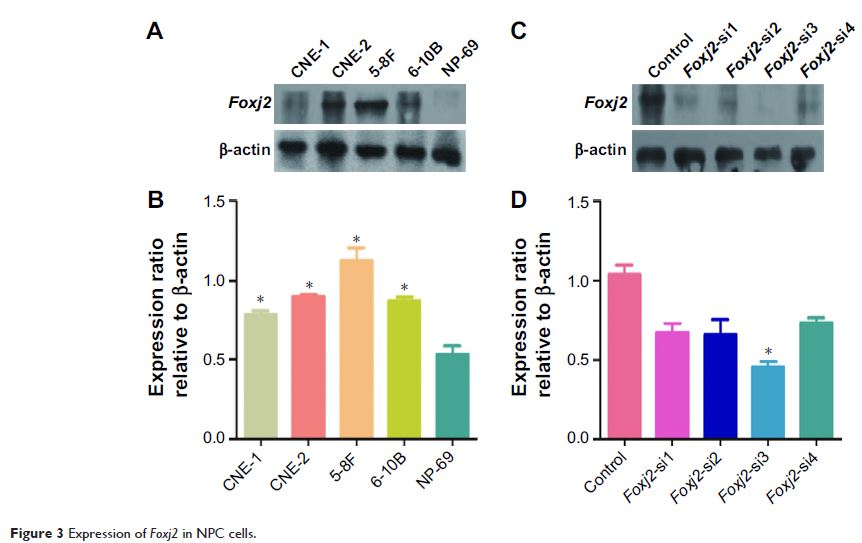
Abstract: Foxj2 , a novel member of Forkhead
box family, has been reported to play an important role in tumorigenesis,
progression, and metastasis of certain cancers. However, the expression status
and effects of Foxj2 on nasopharyngeal
carcinoma (NPC) progression and metastasis remain debated. In this study, we
first examined the expression of Foxj2 in
NPC by immunohistochemistry and Western blotting analysis. We confirmed
significantly elevated expression of Foxj2 in NPC tissues
and cell lines. Next, the relationships between Foxj2 expression levels and
the clinicopathological factors were investigated. Its expression level
correlated with T-classification (P =0.026), distant
metastasis (P =0.004), and clinical stage (P =0.029). In addition, high
expression of Foxj2 was
associated with poor prognosis in NPC patients. The effects of Foxj2 on cell proliferation
and migration were explored by RNA interference (RNAi) with CCK-8 assay, cell
cycle analyses, wound healing, and transwell assay. In conclusion, our data
indicate that Foxj2 upregulation
promotes the progression and migration of NPC. It makes Foxj2 serve as a potential
therapeutic target for the treatment of NPC.
Keywords: Foxj2 , nasopharyngeal carcinoma,
prognosis, progression, migration