109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

用于神经酰胺 IIIB 透皮递送的新型辛基十二烷醇 (octyldodecanol) 纳米乳液的制备、开发和优化
Authors Su R, Yang L, Wang Y, Yu S, Guo Y, Deng J, Zhao Q, Jin X
Received 19 April 2017
Accepted for publication 26 June 2017
Published 21 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5203—5221
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S139975
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: This research aimed to develop and optimize a nanoemulsion-based
formulation containing ceramide IIIB using phase-inversion composition for
transdermal delivery. The effects of ethanol, propylene glycol (PG), and
glycerol in octyldodecanol and Tween 80 systems on the size of the nanoemulsion
region in the phase diagrams were investigated using water titration.
Subsequently, ceramide IIIB loading was kept constant (0.05 wt%), and the
proposed formulation and conditions were optimized via preliminary screening
and experimental design. Factors such as octyldodecanol/(Tween 80:glycerol)
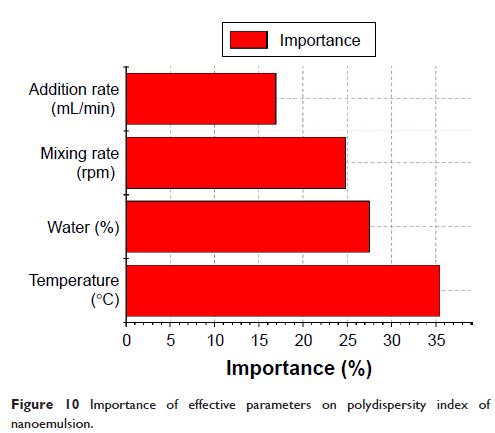
weight ratio, water content, temperature, addition rate, and mixing rate were
investigated in the preliminary screening experiment. Response surface
methodology was employed to study the effect of water content (30%–70%, w/w),
mixing rate (400–720 rpm), temperature (20°C–60°C), and addition rate (0.3–1.8
mL/min) on droplet size and polydispersity index. The mathematical model showed
that the optimum formulation and conditions for preparation of ceramide IIIB
nanoemulsion with desirable criteria were a temperature of 41.49°C, addition
rate of 1.74 mL/min, water content of 55.08 wt%, and mixing rate of 720 rpm.
Under optimum formulation conditions, the corresponding predicted response
values for droplet size and polydispersity index were 15.51 nm and 0.12,
respectively, which showed excellent agreement with the actual values (15.8 nm
and 0.108, respectively), with no significant (P >0.05)
differences.
Keywords: response
surface methodology, nanoemulsions, optimization, particle size, polydispersity
index