109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

miR-203 作为结直肠癌诊断和预后的新型生物标志物:一个系统评价和综合分析
Authors Ye H, Hao H, Wang J, Chen R, Huang Z
Received 8 February 2017
Accepted for publication 22 May 2017
Published 21 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3685—3696
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S134252
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
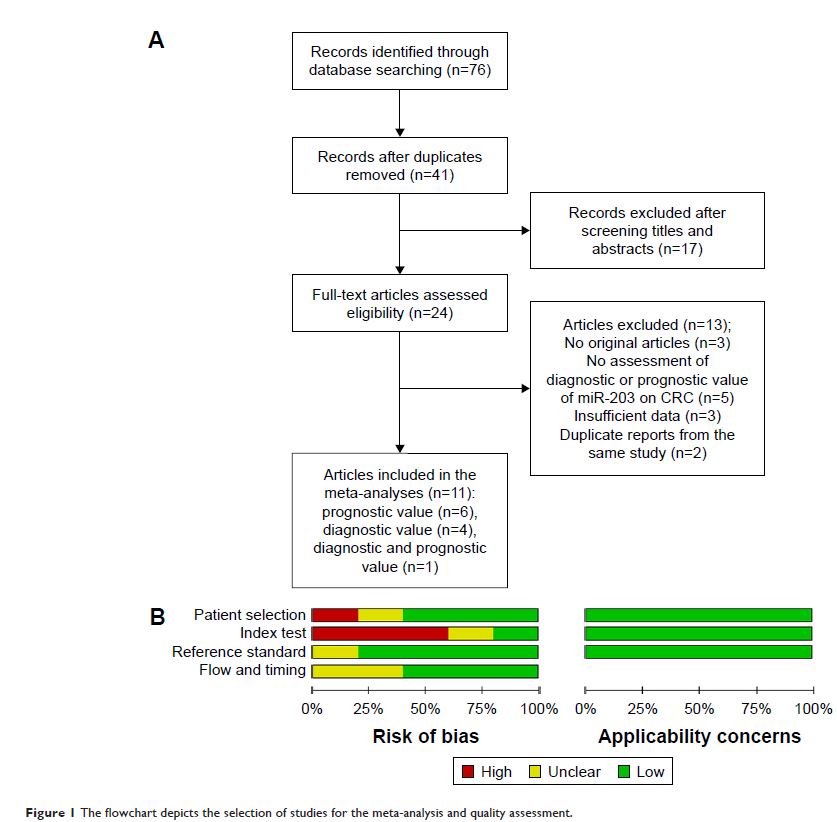
Abstract: We sought to systematically
evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-203 in patients with
colorectal cancer. To explore the diagnostic performance of miR-203, eligible
studies were identified from biomedical databases. Based on these results, 11
studies were pooled and included in this meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity,
specificity, and diagnostic odds ratios of miR-203 were 0.83 (95% confidence
interval, CI: 0.78–0.86), 0.80 (95% CI: 0.77–0.83), and 19.27 (95% CI:
7.23–51.36) for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer. The area under the curve
for miR-203 for diagnosing colorectal cancer was 0.89. Patients with higher
expression of tissue miR-203 had poor overall survival (pooled hazard ratio:
1.63; 95% CI: 1.03–2.57, P =0.04), but serum
miR-203 was not predictive (pooled hazard ratio: 1.59; 95% CI: 0.31–8.12, P =0.58). The miR-203 values
of tissue and serum merged together may perhaps predict superior overall
survival (pooled hazard ratio: 1.62; 95% CI: 0.93–2.82), but the effect was not
significant (P =0.09).
Keywords: colorectal
cancer, CRC, diagnosis, miR-203, prognosis