109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

A54 肽介导的功能化金纳米线用于 DOX 的靶向递送,在肝癌治疗中将光热化疗与化疗结合
Authors Huang S, Li C, Wang WP, Li HJ, Sun Z, Song C, Li B, Duan SF, Hu YR
Received 26 December 2016
Accepted for publication 19 May 2017
Published 20 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5163—5176
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S131089
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Chiara Uboldi
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
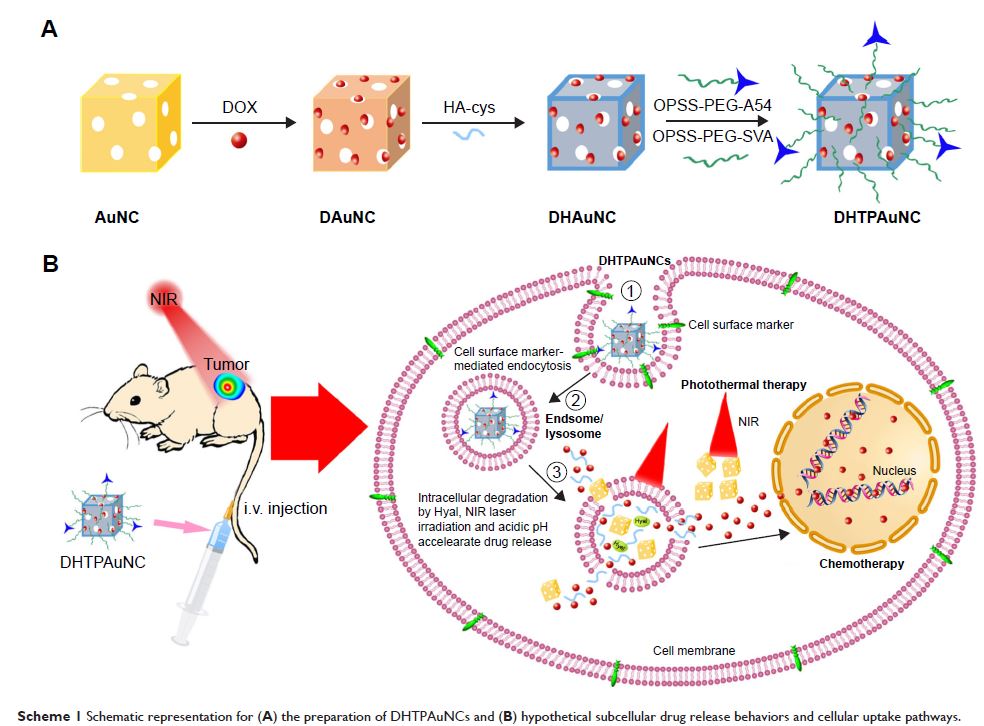
Abstract: The
combination of photothermal therapy and chemotherapy (photothermal–chemotherapy)
is a promising strategy for cancer therapy. Gold nanocages (AuNCs), with hollow
and porous structures and unique optical properties, have become a rising star
in the field of drug delivery. Here, we designed a novel targeted drug delivery
system based on functionalized AuNCs and evaluated their therapeutic effects in
vitro and in vivo. We then loaded doxorubicin into this promising system,
designated as DHTPAuNCs consisting of hyaluronic acid-grafted and A54
peptide-targeted PEGylated AuNCs. Its formation was corroborated by
ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and dynamic
light scattering. This delivery platform needed hyaluronidase to release
encapsulated drugs, meanwhile the acidic pH and near-infrared irradiation could
accelerate the release. In addition, the results of cellular uptake demonstrate
that this system could bind specifically with BEL-7402 cells. In vitro, we
evaluated therapeutic effects of the DHTPAuNCs in BEL-7402 cells by 3-(4,
5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide assay. Moreover, in
BEL-7402 tumor-bearing nude mice, its therapy effect in vivo was also
evaluated. As expected, DHTPAuNCs exhibited excellent therapeutic effect by
photothermal–chemotherapy, both in vitro and in vivo. In short, DHTPAuNCs with
low toxicity showed great potential as a drug delivery system for cancer
therapy.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma, nanocarriers, targeted delivery,
chemotherapy, photothermal therapy