109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

芹菜素 (Apigenin) TPGS 脂质体和酪丝缬肽 (tyroservatide) 的协同凋亡作用:在肺癌有效治疗中的意义
Authors Jin X, Yang Q, Zhang Y
Received 20 April 2017
Accepted for publication 7 June 2017
Published 17 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5109—5118
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S140096
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
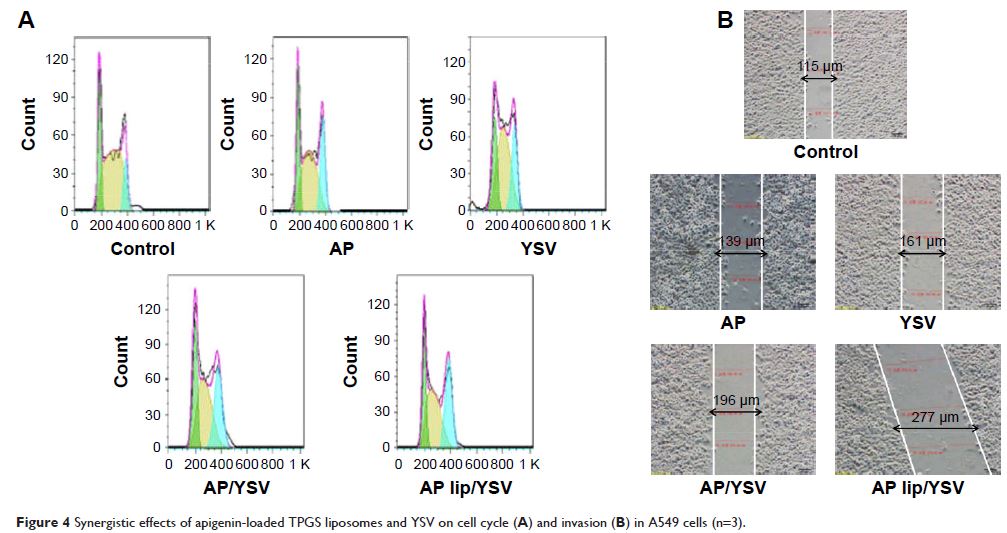
Abstract: To develop an alternative treatment for lung cancer, a combination
of two potent chemotherapeutic agents – liposomal apigenin and tyroservatide –
was developed. The therapeutic potential of this combination was investigated
using A549 cells. Apigenin and tocopherol derivative-containing
D-alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) liposomes might
improve the delivery of apigenin to tumor cells, both in vitro and in vivo.
Importantly, compared to either agent alone, the combination of apigenin TPGS
liposomes and tyroservatide exhibited superior cytotoxicity, induced stronger
G2 arrest, and suppressed A549 cancer cell invasion at a lower dose. The
proapoptotic synergistic effects were also observed in A549 cells using
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling, flow
cytometry, and Western blot analysis. More importantly, in vivo results showed
that the combination of apigenin TPGS liposomes and tyroservatide exhibited
tumor-growth inhibitory effects in A549 cell-bearing mice. In conclusion, our
study showed that this combination therapy could serve as a promising
synergistic therapeutic approach to improve outcomes in patients with lung
cancer.
Keywords: apigenin, TPGS
liposomes, tyroservatide, synergistic antitumor, apoptosis