109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

坐骨神经慢性收缩损伤可改变大鼠脊髓背角的环形 RNA 表达
Authors Cao S, Deng W, Li Y, Qin B, Zhang L, Yu S, Xie P, Xiao Z, Yu T
Received 13 April 2017
Accepted for publication 17 June 2017
Published 17 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1687—1696
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S139592
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
Background: Mechanisms of neuropathic pain are still largely unknown.
Molecular changes in spinal dorsal horn may contribute to the initiation and
development of neuropathic pain. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been identified
as microRNA sponges and involved in various biological processes, but whether
their expression profile changes in neuropathic pain condition is not
reported.
Methods: To test whether neuropathic pain influences circRNA expression, we
developed a sciatic chronic constriction injury (CCI) model in rats. The CCI
ipsilateral spinal dorsal horns of lumbar enlargement segments (L3–L5) were
collected, and the total RNA was extracted and subjected to Arraystar Rat
circRNA Microarray. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was
used to confirm the circRNA expression profile. To estimate functions of
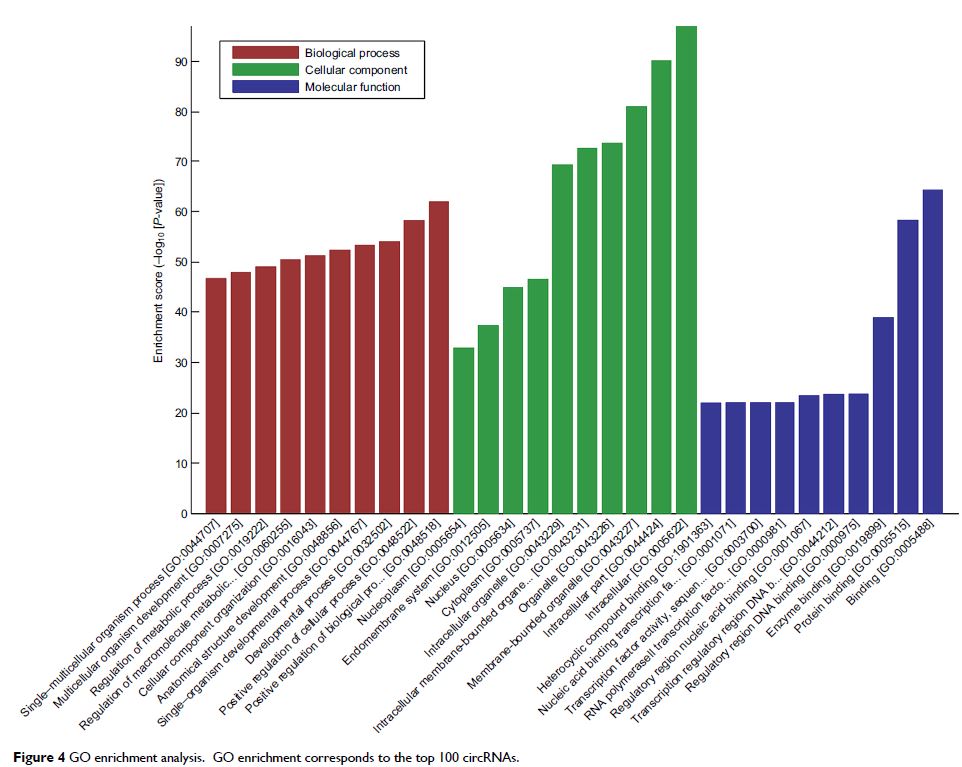
differential circRNAs, bioinformatics analyses including gene ontology (GO) and
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Pathway analyses were performed for the
top 100 circRNAs and circRNA–microRNA networks were constructed for the top 10
circRNAs.
Results: circRNA microarrays showed that 469 circRNAs were differentially
expressed between CCI and sham-operated rats (fold change ≥2). In all, 363 of
them were significantly upregulated, and the other 106 were downregulated in
the CCI group. Three of them (circRNA_013779, circRNA_008008, and
circRNA_003724) overexpressed >10 times after CCI insult. Expression levels
of eight circRNAs were verified using qPCR. GO analysis revealed that thousands
of predicted target genes were involved in the biological processes, cellular
component, and molecular function; in addition, dozens of these genes were
enriched in the Hippo signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, and so on.
Competing endogenous RNAs analysis showed that circRNA_008008 and
circRNA_013779 are the two largest nodes in the circRNA–microRNA interaction
network of the top 10 circRNAs.
Conclusion: CCI resulted in a comprehensive expression profile of circRNAs in
the spinal dorsal horn in rats. CircRNAs in the dorsal horn could be helpful to
reveal molecular mechanisms of neuropathic pain.
Keywords: neuropathic pain, circular RNA, circRNA–microRNA interaction, microarray