109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

白细胞介素-35 作为接受初次前列腺活检患者的前列腺癌预测因素
Authors Zhou CC, Zhang J, Chen Y, Wang H, Hou JQ
Received 1 March 2017
Accepted for publication 25 May 2017
Published 14 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3485—3491
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S135873
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chiung-Kuei Huang
Background: Interleukin (IL)-35 is a novel inhibitory cytokine and has
recently been implicated in tumor immunity. However, the role of IL-35 in
prostate cancer (PCa) has not been elucidated.
Objective: To evaluate the role of plasma IL-35 in the
diagnosis and prognosis of PCa in Chinese patients undergoing initial prostate
biopsy.
Materials and methods: Using ELISA, plasma IL-35 levels were measured
in 180 patients, who underwent a prostate biopsy. The clinical correlation of
IL-35 with clinicopathological parameters was also evaluated. Univariate and
multivariate logistic regression and receiver operating characteristic (ROC)
curve analysis were performed to establish the role of IL-35 as a clinical
biomarker.
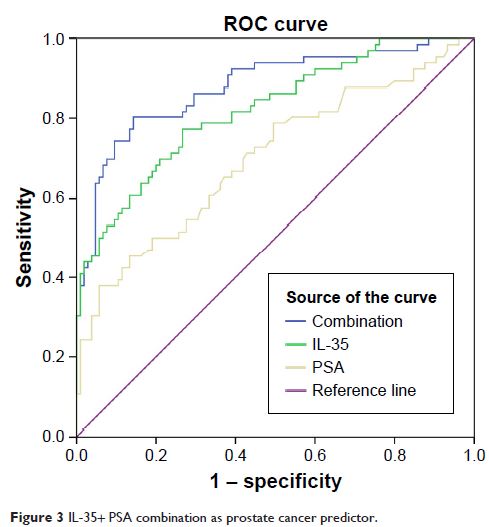
Results: Seventy-five (41.6%) of patients were
histopathologically confirmed to have PCa. Plasma IL-35 levels were
significantly higher in PCa patients (134.48±78.48 pg/mL) compared to non-PCa
patients (67.22±24.08 pg/mL). ROC analysis showed that IL-35 was an independent
predictor of PCa. Furthermore, IL-35 was found to be a significantly
independent predictor of PCa in a group of patients with prostate-specific
antigen levels between 4 and 10 ng/mL; was also able to predict advanced PCa
from localized PCa and bone metastasis positive PCa from negative PCa.
Conclusion: Our data suggest for the first time that plasma
IL-35 levels are correlated with PCa and is the independent predictor of PCa
progression and metastasis. Thus, IL-35 could be utilized as a potential
biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of PCa, could also aid in decision making
and predict the stage of the disease.
Keywords: IL-35, prostate
cancer, prostate biopsy, diagnosis