109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

α-硫辛酸 (α-lipoic acid, ALA) 抑制神经元兴奋性并减弱糖尿病大鼠结直肠扩张的结肠超敏反应
Authors Sun Y, Yang PP, Song ZY, Feng Y, Hu DM, Hu J, Xu GY, Zhang HH
Received 17 February 2017
Accepted for publication 16 May 2017
Published 14 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1645—1655
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S135017
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr E. Alfonso Romero-Sandoval
Aim: Patients with long-standing diabetes often demonstrate intestinal
dysfunction, characterized as constipation or colonic hypersensitivity. Our
previous studies have demonstrated the roles of voltage-gated sodium channels
NaV1.7 and NaV1.8 in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) in colonic hypersensitivity of
rats with diabetes. This study was designed to determine roles of antioxidant
α-lipoic acid (ALA) on sodium channel activities and colonic hypersensitivity
of rats with diabetes.
Methods: Streptozotocin was used to induce diabetes in adult
female rats. Colonic sensitivity was measured by behavioral responses to
colorectal distention in rats. The excitability and sodium channel currents of
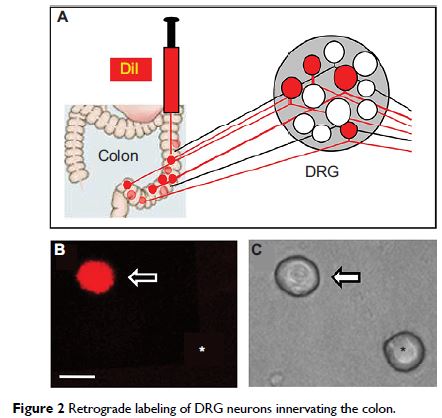
colon projection DRG neurons labeled with DiI were measured by whole-cell
patch-clamp recordings. The expressions of NaV1.7 and NaV1.8 of colon DRGs were
measured by western blot analysis.
Results: ALA treatment significantly increased distention
threshold in responding to colorectal distension in diabetic rats compared with
normal saline treatment. ALA treatment also hyperpolarized the resting membrane
potentials, depolarized action potential threshold, increased rheobase, and
decreased frequency of action potentials evoked by ramp current stimulation.
Furthermore, ALA treatment also reduced neuronal sodium current densities of
DRG neurons innervating the colon from rats with diabetes. In addition, ALA
treatment significantly downregulated NaV1.7 and NaV1.8 expression in colon
DRGs from rats with diabetes.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that ALA plays an analgesic role,
which was likely mediated by downregulation of NaV1.7 and NaV1.8 expressions
and functions, thus providing experimental evidence for using ALA to treat
colonic hypersensitivity in patients with diabetic visceral pain.
Keywords: diabetes,
colonic hypersensitivity, dorsal root ganglion, voltage-gated sodium channels,
α-lipoic acid