109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于比色测定转化为电化学分析,并利用双链特异性核酸酶的信号放大技术,进行微小 RNA 的灵敏检测
Authors Xia N, Liu K, Zhou Y, Li Y, Yi X
Received 2 April 2017
Accepted for publication 13 June 2017
Published 13 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 5013—5022
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S138656
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
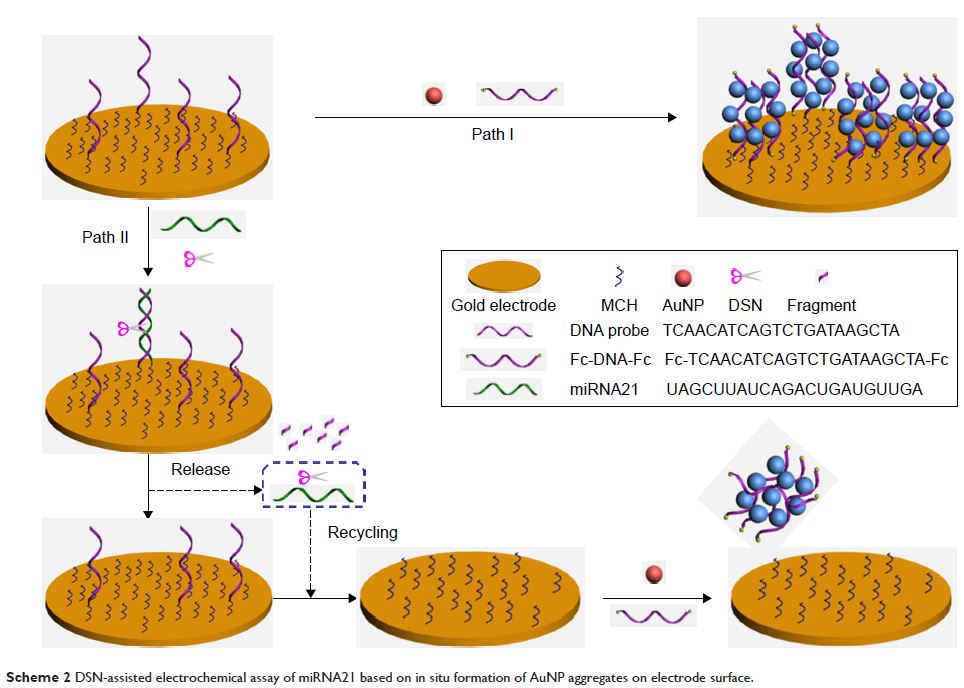
Abstract: miRNAs
have emerged as new biomarkers for the detection of a wide variety of cancers.
By employing duplex-specific nuclease for signal amplification and gold
nanoparticles (AuNPs) as the carriers of detection probes, a novel
electrochemical assay of miRNAs was performed. The method is based on
conversion of the well-known colorimetric assay into electrochemical analysis
with enhanced sensitivity. DNA capture probes immobilized on the electrode
surface and ferrocene (Fc)-labeled DNA detection probes (denoted “Fc-DNA-Fc”)
presented in the solution induced the assembly of positively charged AuNPs on
the electrode surface through the electrostatic interaction. As a result, a
large number of Fc-DNA-Fc molecules were attached on the electrode surface,
thus amplifying the electrochemical signal. When duplex-specific nuclease was
added to recycle the process of miRNA-initiated digestion of the immobilized
DNA probes, Fc-DNA-Fc-induced assembly of AuNPs on the electrode surface could
not occur. This resulted in a significant fall in the oxidation current of Fc.
The current was found to be inversely proportional to the concentration of
miRNAs in the range of 0–25 fM, and a detection limit of 0.1 fM was achieved.
Moreover, this work presents a new method for converting colorimetric assays
into sensitive electrochemical analyses, and thus would be valuable for design
of novel chemical/biosensors.
Keywords: microRNA, duplex-specific nuclease, gold nanoparticle, signal
amplification, electrochemical biosensor, colorimetric assay