109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PD-1 阻断可恢复体外扩增 CD8+ T 细胞受损的功能,促进错配修复缺陷 EpCAM+PD-L1+ 癌细胞的凋亡
Authors Kumar R, Yu F, Zhen YH, Li B, Wang J, Yang Y, Ge HX, Hu P, Xiu J
Received 13 December 2016
Accepted for publication 27 May 2017
Published 13 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3453—3465
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S130131
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashok Kumar Pandurangan
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
Background: Adoptive T cell therapy has been proven to be a promising modality
for the treatment of cancer patients in recent years. However, the increased
expression of inhibitory receptors could negatively regulate the function and
persistence of transferred T cells which mediates T cell anergy, exhaustion,
and tumor regression. In this study, we investigated increased cytotoxic
activity after the blockade of PD-1 for effective immunotherapy.
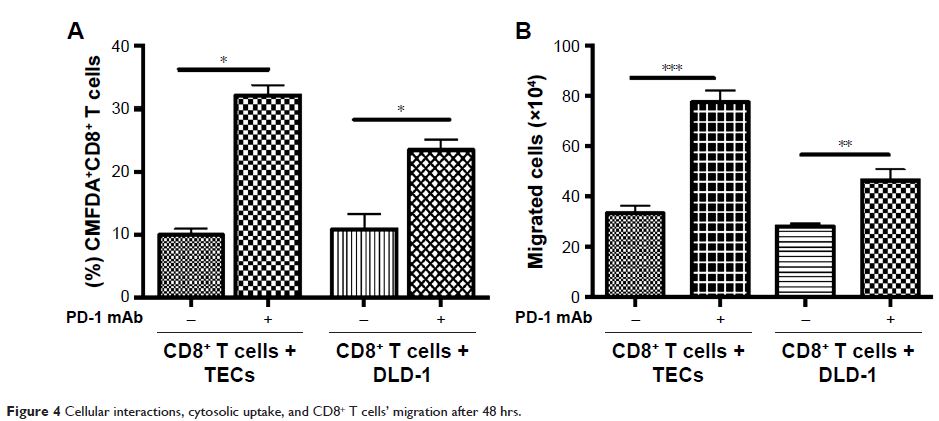
Methods: The cytotoxic function of expanded CD8+ CTLs and interactions with tumor cells
investigated after blocking of PD-1. Ex vivo expanded CD8+ CTLs were co-cultured with mismatch repair
(MMR) stable or deficient (high microsatellite instability [MSI-H]) EpCAM+ tumor cells. The levels of IFN-γ and GrB were
detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assay. Flow cytometry and confocal
microscopy were used to assess CD107a mobilization, cytosolic uptake, and cell
migration.
Results: A dramatic increase in PD-1 expression on the
surface of CD8+ CTLs during ex vivo
expansion was observed. PD-1 level was downregulated by approximately 40% after
incubation of the CD8+ CTLs with monoclonal
antibody which enhanced the secretion of IFN-γ, GrB, and CD107a. Additionally,
PD-1 blockade enhanced cell migration and cytosolic exchange between CD8+ CTLs and MMR deficient (MSI-H) EpCAM+PD-L1+ tumor
cells.
Conclusion: The blockade of PD-1 enhanced the cytotoxic efficacy
of CD8+ CTLs toward MMR deficient tumor cells. In
conclusion, we propose that blocking of PD-1 during the expansion of CD8+ CTLs
may improve the clinical efficacy of cell-based adoptive immunotherapy.
Keywords: PD-1, CTLs,
MSI-H, EpCAM+PD-L1+, cancer
immunotherapy