109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

DNA 修复基因 XRCC1 的多态性与非黑色素瘤皮肤癌风险的关系:一项综合分析
Authors Wang L, Xu J, Duan B
Received 5 February 2017
Accepted for publication 16 May 2017
Published 13 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3475—3483
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S133978
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Chiung-Kuei Huang
Objective: Non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC) is the most common malignancy with
annually rising incidence. The aim of this study was to estimate the
association between three coding polymorphisms (Arg399Gln, Arg194Trp, and
Arg280His) of the DNA repair gene X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1
(XRCC1) and NMSC susceptibility.
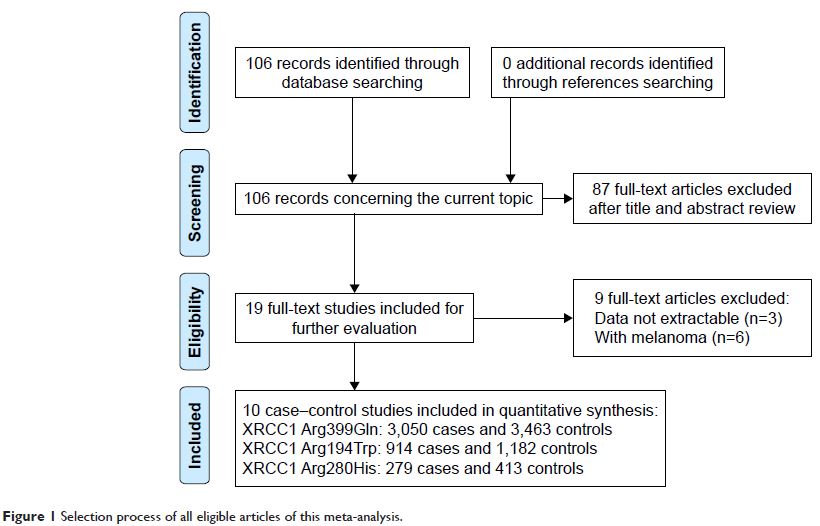
Methods: Online databases were searched to retrieve
case–control studies published between January 2000 and November 2016. Pooled
odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were employed to assess the
strength of association. Overall, 10 relevant studies were finally included for
analysis, including 3,143 NMSC patients and 3,540 controls. For each
polymorphism of XRCC1 gene,
there were 3,050 cases and 3,463 controls for Arg399Gln, 914 cases and 1,182
controls for Arg194Trp, and 279 cases and 413 controls for Arg280His.
Results: Our results showed that these three polymorphisms in
the XRCC1 coding region were not associated with increased risk of NMSC in the
total studied population. However, subgroup analysis by ethnicities
demonstrated that Gln/Arg genotype of Arg399Gln polymorphism was associated
with increased risk of NMSC under the heterogeneous model in Asian populations
(Gln/Arg vs Arg/Arg: OR =1.39, 95% CI =1.04–1.87, P =0.03); subgroup analysis by
tumor types showed that Trp/Trp genotype of Arg194Trp was positively associated
with decreased cancer risk in squamous-cell skin cancer (SCC) type under the
homogeneous model (Trp/Trp vs Arg/Arg: OR =0.38, 95% CI =0.16–0.92, P =0.03).
Conclusion: Our results suggested that Arg399Gln variant of XRCC1 gene might be a risk
factor for NMSC in Asian populations, and Arg194Trp variant of XRCC1 gene might be a
protective factor for patients with SCC. In addition, future case–control
studies are still needed to further evaluate the effect of XRCC1 polymorphisms
in NMSC risk.
Keywords: non-melanoma
skin cancer, XRCC1, polymorphism, meta-analysis, DNA repair, risk factor