109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用聚合物纳米胶囊全面递送抗癌剂沙蟾毒精 (Arenobufagin)
Authors Yuan X, Xie Q, Su K, Li Z, Dong D, Wu B
Received 7 April 2017
Accepted for publication 23 May 2017
Published 12 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4981—4989
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S139128
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Arenobufagin (ABG) is a
major active component of toad venom, a traditional Chinese medicine used for
cancer therapy. However, poor aqueous solubility limits its pharmacological
studies in vivo due to administration difficulties. In this study, we aimed to
develop a polymeric nanomicelle (PN) system to enhance the solubility of ABG
for effective intravenous delivery. ABG-loaded PNs (ABG-PNs) were prepared with
methoxy poly (ethylene glycol)-block-poly (D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid)
(mPEG-PLGA) using the solvent-diffusion technique. The obtained ABG-PNs were
105 nm in size with a small polydispersity index of 0.08. The entrapment
efficiency and drug loading were 71.9% and 4.58%, respectively. Cellular uptake
of ABG-PNs was controlled by specific clathrin-mediated endocytosis. In
addition, ABG-PNs showed improved drug pharmacokinetics with an increased area
under the curve value (a 1.73-fold increase) and a decreased elimination
clearance (37.8% decrease). The nanomicelles showed increased drug
concentrations in the liver and lung. In contrast, drug concentrations in both
heart and brain were decreased. Moreover, the nanomicelles enhanced the
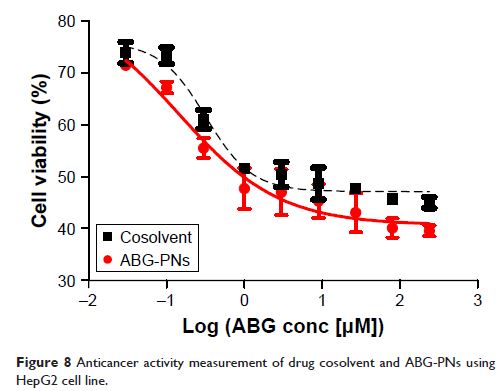
anticancer effect of the pure drug probably via increased cellular uptake of
drug molecules. In conclusion, the mPEG-PLGA-based nanomicelle system is a
satisfactory carrier for the systemic delivery of ABG.
Keywords: bufanolide
steroid, arenobufagin, nanomicelles, mPEG-PLGA