109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对葡萄膜黑色素瘤病例中 p53 基因表达和预后特征的评估
Authors Liu H, Zhou M
Received 11 March 2017
Accepted for publication 22 April 2017
Published 12 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3429—3434
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S136785
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Narasimha Reddy Parine
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Carlos Vigil Gonzales
Objective: The
objective of this study was to evaluate the correlation between the expression
of p53 gene and the prognosis after
local excision in uveal melanoma.
Materials and
methods: Real-time polymerase chain
reaction (RT-PCR) test and Western blot were used to detect the expression of
p53 in C918, MUM-2B, and D78 cell lines at the levels of messenger RNA (mRNA)
and protein. Immunohistochemistry staining was done in the tissues of 68
patients, which were diagnosed with uveal melanoma. Furthermore, the effects of
p53 protein on the invasion abilities of both the cell lines were studied by
transinfection of p53 small interfering RNA. The clinical and prognostic data
regarding the effect of p53 protein on the patient’s prognosis were calculated
and further analyzed by Kaplan–Meier univariate analysis method.
Results: The results of RT-PCR and Western blot revealed that p53 mRNAs were
highly expressed in C918 and MUM-2B cells. The high expression rate of p53
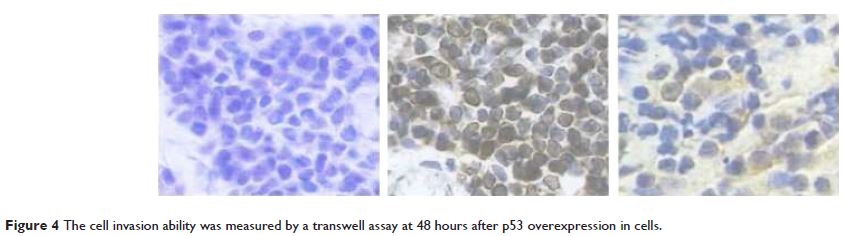
among the 88 uveal melanoma tissues was 77.27%. Transinfection of p53 serine could
inhibit the expression of p53 in uveal melanoma and the invasion ability of the
cells. This study found that the high expression of p53 and the prognosis of
uveal melanoma patients were statistically correlated.
Conclusion: The expression of p53 protein in uveal melanoma was unusual and was
associated with the invasion ability of uveal melanoma. This indicates that the
highest expression of p53 protein indicates worse prognosis of uveal melanoma
patients.
Keywords: uveal melanoma, PCR, prognosis, Western blot, immunohistochemistry