109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

The ABC7 regimen: a new approach to metastatic breast cancer using seven common drugs to inhibit epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and augment capecitabine efficacy
Authors Kast RE, Skuli N, Cos S, Karpel-Massler G, Shiozawa Y, Goshen R, Halatsch ME
Received 19 April 2017
Accepted for publication 22 May 2017
Published 11 July 2017 Volume 2017:9 Pages 495—514
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/BCTT.S139963
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Pranela Rameshwar
Abstract: Breast cancer metastatic to bone has a poor prognosis despite
recent advances in our understanding of the biology of both bone and breast
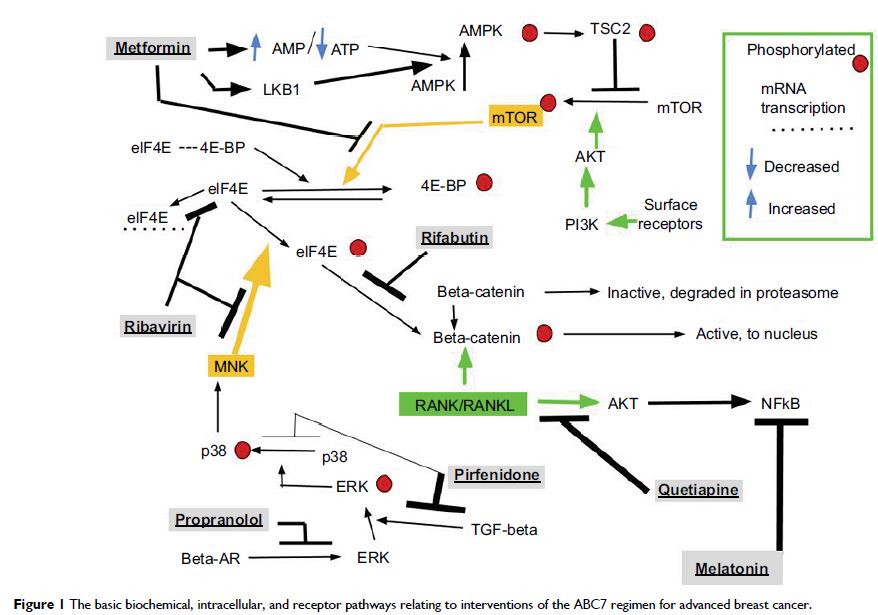
cancer. This article presents a new approach, the ABC7 regimen (Adjuvant for
Breast Cancer treatment using seven repurposed drugs), to metastatic breast
cancer. ABC7 aims to defeat aspects of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
(EMT) that lead to dissemination of breast cancer to bone. As add-on to current
standard treatment with capecitabine, ABC7 uses ancillary attributes of seven
already-marketed noncancer treatment drugs to stop both the natural EMT process
inherent to breast cancer and the added EMT occurring as a response to current
treatment modalities. Chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery provoke EMT in
cancer generally and in breast cancer specifically. ABC7 uses standard doses of
capecitabine as used in treating breast cancer today. In addition, ABC7 uses 1)
an older psychiatric drug, quetiapine, to block RANK signaling; 2) pirfenidone,
an anti-fibrosis drug to block TGF-beta signaling; 3) rifabutin, an antibiotic
to block beta-catenin signaling; 4) metformin, a first-line antidiabetic drug
to stimulate AMPK and inhibit mammalian target of rapamycin, (mTOR); 5)
propranolol, a beta-blocker to block beta-adrenergic signaling; 6) agomelatine,
a melatonergic antidepressant to stimulate M1 and M2 melatonergic receptors;
and 7) ribavirin, an antiviral drug to prevent eIF4E phosphorylation. All these
block the signaling pathways – RANK, TGF-beta, mTOR, beta-adrenergic receptors,
and phosphorylated eIF4E – that have been shown to trigger EMT and enhance
breast cancer growth and so are worthwhile targets to inhibit. Agonism at MT1
and MT2 melatonergic receptors has been shown to inhibit both breast cancer EMT
and growth. This ensemble was designed to be safe and augment capecitabine
efficacy. Given the expected outcome of metastatic breast cancer as it stands
today, ABC7 warrants a cautious trial.
Keywords: ABC7, breast cancer, agomelatine, capecitabine, metformin,
pirfenidone, propranolol, quetiapine, repurposing, ribavirin, rifabutin,
TGF-beta