109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA CASC2 预测胶质瘤患者的预后,并通过抑制 Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路成为胶质瘤抑制因子
Authors Wang R, Li Y, Zhu G, Tian B, Zeng W, Yang Y, Li Z
Received 16 March 2017
Accepted for publication 5 May 2017
Published 11 July 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 1805—1813
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S137171
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Prof. Dr. Roumen Kirov
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Background: Previous studies have demonstrated that long noncoding RNA cancer
susceptibility candidate 2 (lncRNA CASC2) is frequently downregulated in
several types of tumors and functions as a tumor-suppressive factor. However,
the clinical significance and function of CASC2 in human glioma remain largely
unknown. The purpose of this study was to identify the clinical values of
CASC2, as well as investigate the potential molecular mechanisms in glioma.
Methods: This retrospective study first analyzed the
expression levels of CASC2 using quantitative real-time polymerase chain
reaction. Then, CASC2 expression levels were associated with various
clinicopathologic characteristics and the survival rate of patients with
glioma. Finally, the function and underlying molecular mechanisms of CASC2 in
human glioma were investigated in U251 cell line.
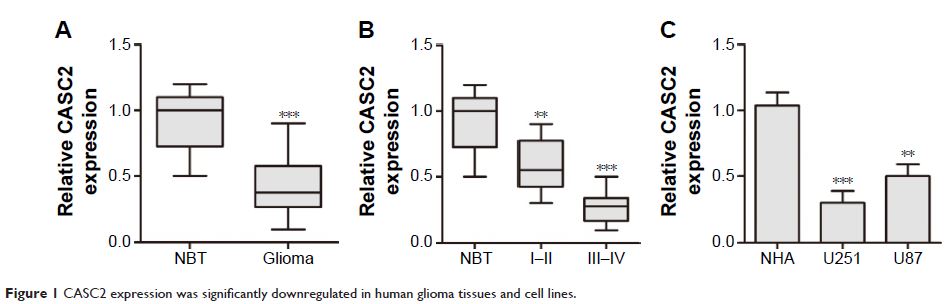
Results: By quantitative real-time polymerase chain
reaction analysis, our data showed that CASC2 expression was significantly
downregulated in glioma tissues and cell lines (U87 and U251) compared to
adjacent normal brain tissues or normal human astrocytes. Moreover, its
expression negatively correlated with tumor grade in glioma patients.
Furthermore, Kaplan–Meier curves with log-rank analysis revealed a close
correlation between downregulated CASC2 and shorter survival time in glioma
patients. In addition, Cox regression analysis indicated that CASC2 could be
considered as an independent risk factor for poor prognosis. Finally, in vitro
experiment demonstrated that CASC2 overexpression remarkably suppressed glioma
cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through suppressing Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway.
Conclusion: This study suggested that CASC2 may potentially
serve as a valuable diagnostic and prognostic biomarker and a therapeutic
target for glioma patients.
Keywords: glioma, lncRNA,
CASC2, biomarker, Wnt/β-catenin