109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

13C 骨架标记碳纳米粒子用于肿瘤引流淋巴结的成像和定量
Authors Xie P, Xin Q, Yang S, He T, Huang Y, Zeng G, Ran M, Tang XH
Received 11 February 2017
Accepted for publication 10 April 2017
Published 11 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4891—4899
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S134493
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Carbon nanoparticles (CNPs) have been widely used in tumor
drainage lymph node (TDLN) imaging, drug delivery, photothermal therapy, and so
on. However, during the theranostic applications, the accumulation efficiency
of CNPs in target organs is unknown yet, which largely hinders the extension of
CNPs into clinical uses. Herein, we prepared skeleton-labeled 13C-CNPs that had identical properties to commercial
CNPs suspension injection (CNSI) for the imaging and quantification in
TDLN. 13C-CNPs were prepared by arc discharge method,
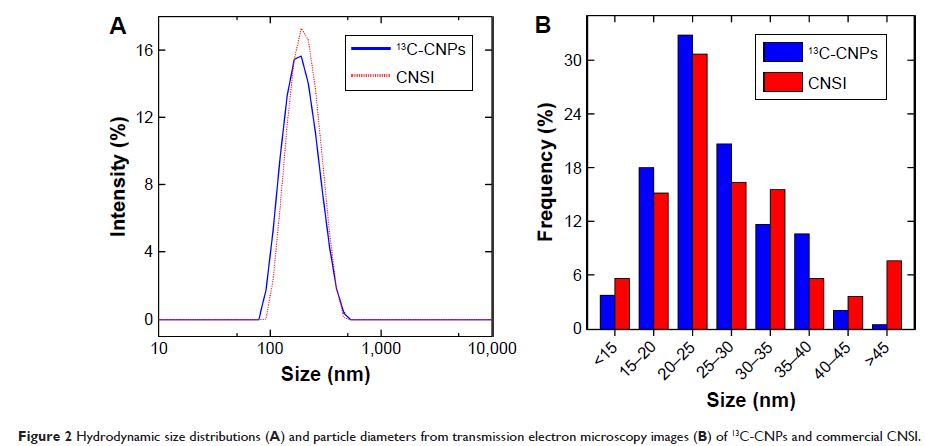
followed by homogenization with polyvinylpyrrolidone. The size distribution and
morphology of 13C-CNPs were nearly the same as
those of CNSI under transmission electron microscope. The hydrodynamic radii of
both 13C-CNPs and CNSI were similar, too. According
to X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy analyses, the
chemical compositions and chemical states of elements were also nearly
identical for both labeled and commercial forms. The skeleton labeling of 13C was reflected by the shift of G-band toward lower
frequency in Raman spectra. 13C-CNPs showed
competitive performance in TDLN imaging, where the three lymph nodes (popliteal
lymph node, common iliac artery lymph node, and paraaortic lymph node) were
stained black upon the injection into the hind extremity of mice. The direct
quantification of 13C-CNPs indicated
that 877 µg/g of 13C-CNPs
accumulated in the first station of TDLN (popliteal lymph node). The second
station of TDLN (common iliac artery lymph node) had even higher accumulation
level (1,062 µg/g), suggesting that 13C-CNPs migrated
efficiently along lymphatic vessel. The value decreased to 405 µg/g in the
third station of TDLN (paraaortic lymph node). Therefore, the 13C-CNPs provided quantitative approach to image and
quantify CNSI in biological systems. The implication in biomedical applications
and biosafety evaluations of CNSI is discussed.
Keywords: carbon
nanoparticles suspension injection, 13C-labeling,
isotope ratio mass spectroscopy, quantification, bioeffect of nanomaterials