108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

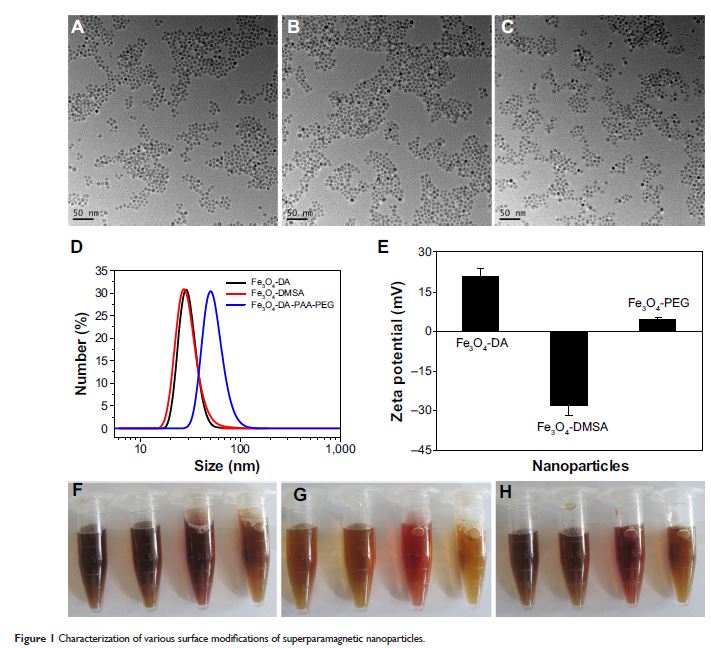
四氧化三铁纳米粒通过调节 Beclin 1 / Bcl-2/ VPS34 复合诱导人类血细胞促存活细胞自噬
Authors Shi M, Cheng L, Zhang Z, Liu Z, Mao X
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2015:10 Pages 207—216
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S72598
Received 12 August 2014, Accepted 27 September 2014, Published 24 December 2014
Abstract: Magnetic
iron oxide nanoparticles (NPs) are emerging as novel materials with great
potentials for various biomedical applications, but their biological activities
are largely unknown. In the present study, we found that ferroferric oxide
nanoparticles (Fe3O4 NPs) induced autophagy in blood
cells. Both naked and modified Fe3O4 NPs induced LC3
lipidation and degraded p62, a monitor of autophagy flux. And this change could
be abolished by autophagy inhibitors. Mechanistically, Fe3O4 NP-induced autophagy was accompanied by increased Beclin 1 and VPS34 and
decreased Bcl-2, thus promoting the formation of the critical complex in
autophagy initiation. Further studies demonstrated that Fe3O4 NPs attenuated cell death induced by anticancer drugs bortezomib and doxorubicin.
Therefore, this study suggested that Fe3O4 NPs can induce
prosurvival autophagy in blood cells by modulating the Beclin l/Bcl-2/VPS34
complex. This study suggests that caution should be taken when Fe3O4 NPs are used in blood cancer patients.
Keywords: iron oxide
nanoparticle, autophagic pathway, anti-apoptosis