109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

RNA 测序可鉴定 U2OS 骨肉瘤细胞中与 β-雌二醇治疗相关的基因表达谱变化
Authors Chen B, Liu Z, Zhang J, Wang H, Yu B
Received 22 February 2017
Accepted for publication 27 May 2017
Published 11 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3421—3427
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S135396
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Narasimha Reddy Parine
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Tohru Yamada
Abstract: This
study was conducted to identify gene expression profile changes associated with
β-estradiol (E2) treatment in U2OS osteosarcoma cells by high-throughput RNA
sequencing (RNA-seq). Two U2OS cell samples treated with E2 (15 µmol/L)
and two untreated control U2OS cell samples were subjected to RNA-seq. Differentially
expressed genes (DEGs) between the groups were identified, and main biological
process enrichment was performed using gene ontology (GO) analysis. A
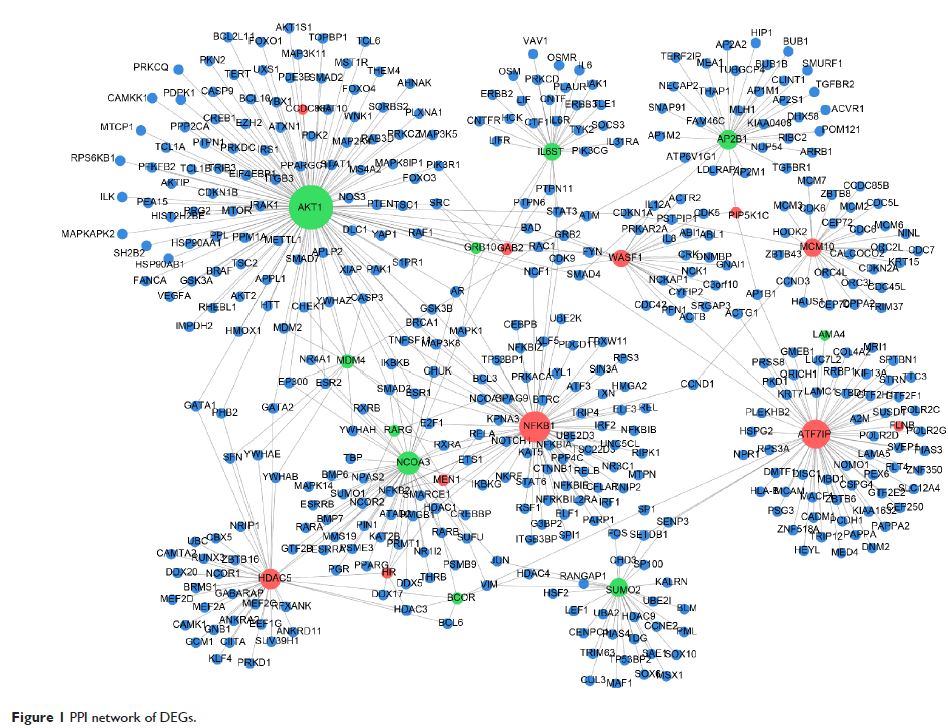
protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed using Cytoscape based
on the Human Protein Reference Database. Finally, NFKB1 expression was
confirmed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The
map ratios of the four sequenced samples were >65%. In total, 128
upregulated and 92 downregulated DEGs were identified in E2 samples. After GO
enrichment, the downregulated DEGs, such as AKT1 ,
were found to be mainly enriched in cell cycle processes, whereas the
upregulated DEGs, such as NFKB1 , were
involved in the regulation of gene expression. Moreover, AKT1 (degree =117) and
NFKB1 (degree =72) were key nodes with the highest degrees in the PPI network.
Similarly, the results of qRT-PCR confirmed that E2 upregulated NFKB1 expression. The results
suggest that E2 upregulates the expression of NFKB1 , ATF7IP , and HDAC5 , all of which are involved
in the regulation of gene expression and transcription, but downregulates that
of TCF7L2 , ALCAM , and AKT , which are involved in Wnt
receptor signaling through β-catenin and morphogenesis in U2OS osteosarcoma
cells.
Keywords: differentially expressed genes, Wnt receptor signaling, β-catenin,
protein-protein interaction network