109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对 miR-144-3p 在肝细胞癌中的临床病理学意义的全面了解
Authors Liang HW, Ye ZH, Yin SY, Mo WJ, Wang HL, Zhao JC, Liang GM, Feng ZB, Chen G, Luo DZ
Received 28 March 2017
Accepted for publication 10 June 2017
Published 11 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3405—3419
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S138143
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Background: Studies which focused on the character of miR-144-3p in hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) are limited. This study aimed to explore the expression,
clinical significance and the potential targets of miR-144-3p in HCC.
Methods: The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and a cohort of 95
cases of HCC were applied to investigate aberrant miR-144-3p expression in HCC.
A meta-analysis was performed to accumulate data on miR-144-3p expression in
HCC based on TCGA, quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
(qRT-PCR) and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Additionally, the potential
regulatory mechanisms of miR-144-3p in HCC were explored by bioinformatics.
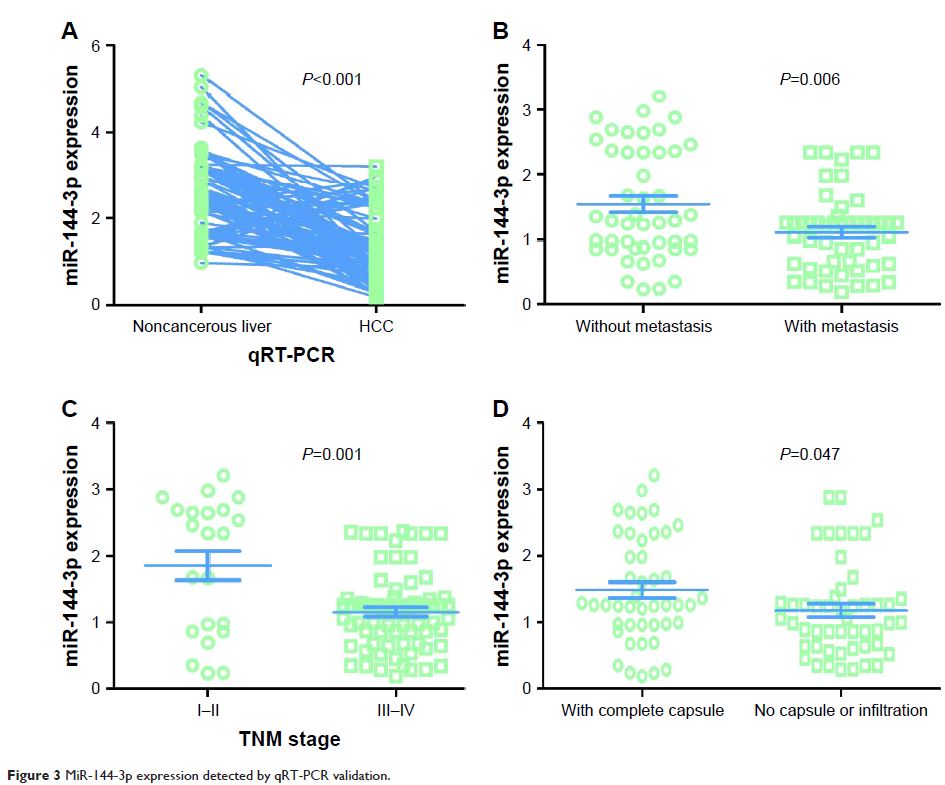
Results: MiR-144-3p expression was downregulated distinctly in
HCC compared to para-HCC tissue both in TCGA data (8.9139±1.5986 vs 10.7721±0.9156, P <0.001) and in our qRT-PCR
validation (1.3208±0.7594 vs 2.6200±0.9263, P <0.001).
The meta-analysis based on TCGA, qRT-PCR and GEO data confirmed a consistent
result (standard mean difference =-0.854, 95% CI: -1.224 to -0.484, P <0.001). The receiver
operating characteristic curve of miR-144-3p gained a significant diagnostic
value both in TCGA data (area under the curve [AUC] =0.852, 95% CI: 0.810 to
0.894, P <0.001) and in qRT-PCR
validation (AUC =0.867, 95% CI: 0.817 to 0.916, P <0.001), especially in
alpha-fetoprotein–negative HCC patients (AUC =0.900, 95% CI: 0.839 to
0.960, P <0.001). Furthermore, we
identified 119 potential targets of miR-144-3p in HCC by bioinformatics. Gene
ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analyses revealed
that several significant biologic functions and pathways correlated with the
pathogenesis of HCC, including the p53 signaling pathway.
Conclusion: MiR-144-3p may function as a cancer suppressor
microRNA, which is essential for HCC progression through the regulation of
various signaling pathways. Thus, interactions with miR-144-3p may provide a
novel treatment strategy for HCC in the future.
Keywords: miR-144-3p,
hepatocellular carcinoma, TCGA, qRT-PCR, GEO, gene functional enrichment
analysis