108605
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

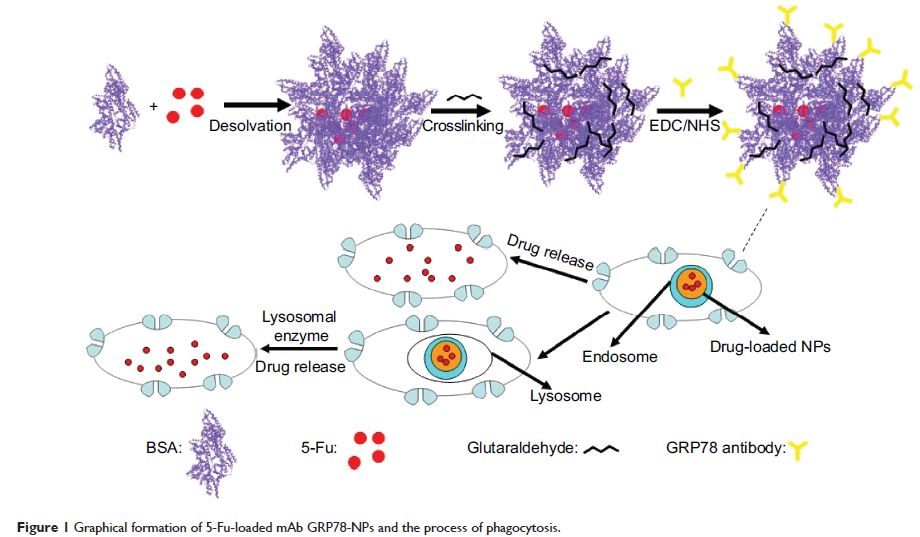
纳米粒抑制癌细胞的侵袭和通过细胞表面 GRP78 增强靶向给药的抗肿瘤疗效
Authors Zhao L, Li H, Shi Y, Wang G, Liu L, Su C, Su R
Published Date December 2014 Volume 2015:10 Pages 245—256
DOI http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S74868
Received 24 September 2014, Accepted 9 November 2014, Published 30 December 2014
Abstract: Nanoparticles (NPs) which target specific agents could effectively recognize
the target cells and increase the stability of chemical agents by
encapsulation. As such, NPs have been widely used in cancer treatment research.
Recently, over 90% of treatment failure cases in patients with metastatic
cancer were attributed to resistance to chemotherapy. Surface-exposed
glucose-regulated protein of 78 kDa (GRP78) is expressed highly on many tumor
cell surfaces in many human cancers and is related to the regulation of
invasion and metastasis. Herein, we report that NPs conjugated with antibody
against GRP78 (mAb GRP78-NPs) inhibit the adhesion, invasion, and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and promote drug delivery of 5-fluorouracil into
GRP78 high-expressed human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Our new findings
suggest that mAb GRP78-NPs could enhance drug accumulation by effectively
transporting NPs into cell surface GRP78-overexpressed human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells and then inhibit cell proliferation and viability and induce
cell apoptosis by regulating caspase-3. In brief, mAb GRP78-NPs effectively
inhibit cancer cell invasion and enhance antitumor efficiency by targeted drug
delivery.
Keywords: 5-Fu, apoptosis, HCC,
caspase-3