109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用肿瘤组织或血液的常规实时、基于 PCR 的 T790M 检测方法用于对 EGFR TKI 耐药的 NSCLC 患者
Authors Wu Y, Tong R, Zhang Y, Hu B, Zheng K, Ding Z, Peng F, Gong Y, Liu Y, Lu Y
Received 12 March 2017
Accepted for publication 6 June 2017
Published 5 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 3307—3312
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S136823
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Narasimha Reddy Parine
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ingrid Espinoza
Abstract: Blood biopsy has many advantages over tissue biopsy for diagnosing
acquired T790M mutation in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer, such as
being less risky and painful. New techniques with high sensitivity (eg, droplet
digital PCR) show promising results during blood biopsy, but the positive rates
of identification are still quite unclear. Whether there are other factors,
except technology, affecting the results of blood biopsy is unclear. In this
study, we used conventional amplification refractory mutation system to detect
tumor tissue or blood for T790M mutation in patients clinically resistant to
tyrosine kinase inhibitors. A total of 45 patients treated at West China Hospital
between 2014 and 2016 were analyzed. The positive rate of T790M mutation was
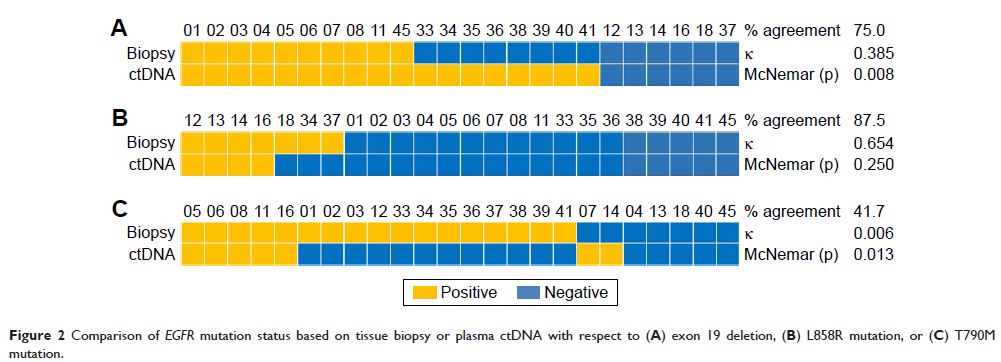
70.8% based on tissue biopsy and 37.5% based on blood biopsy. Of the 24
patients whose epidermal growth factor receptor gene was genotyped through
tissue and blood biopsy, 10 (41.7%) were concordant for T790M mutation status
(κ=0.006). Of the 17 patients positive for T790M by tissue biopsy, 7 (41.2%)
were positive for T790M by blood biopsy, and 3 of these 7 were only weakly
positive. Of the 7 patients negative for T790M by tissue biopsy, 2 (28.6%) were
positive by blood biopsy. Our T790M detection rate is higher than that reported
by other studies using digital droplet PCR. These results suggest that other
factors (eg, clinical features), intrinsically connected with circulating tumor
DNA level, also affect the results of blood biopsy, and thus cannot be
controlled through technological optimization.
Keywords: non-small-cell
lung cancer, T790M mutation, re-biopsy, liquid biopsy