109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过可溶解、基于微针阵列的递送系统与亚单位疫苗及皂苷 (Saponin) 佐剂相结合来增强免疫
Authors Zhao JH, Zhang QB, Liu B, Piao XH, Yan YL, Hu XG, Zhou K, Zhang YT, Feng NP
Received 15 January 2017
Accepted for publication 18 April 2017
Published 4 July 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 4763—4772
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S132456
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Purpose: To enhance the immunogenicity of the model subunit vaccine,
ovalbumin (OVA) was combined with platycodin (PD), a saponin adjuvant. To
reduce the toxicity of PD, OVA, and adjuvant were loaded together into
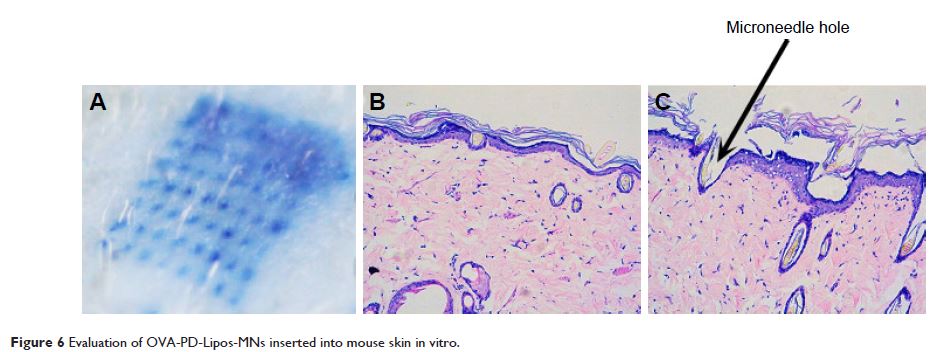
liposomes before being incorporated into a dissolving microneedle array.
Methods: OVA- and PD-loaded liposomes (OVA-PD-Lipos) were
prepared using the film dispersion method. Their uptake behavior, toxicity to
mouse bone marrow dendritic cells (BMDCs), and hemolytic activity to rabbit red
blood cells (RBCs) were evaluated. The OVA-PD-Lipos were incorporated into a
dissolving microneedle array. The chemical stability of OVA and the physical
stability of OVA-PD-Lipos in microneedle arrays were investigated. The immune
response of Institute of Cancer Research mice and potential skin irritation
reaction of rabbits to OVA-PD-Lipos-MNs were evaluated.
Results: The uptake of OVA by mouse BMDCs was greatly
enhanced when OVA was prepared as OVA-PD-Lipos, and in this form, the toxicity
of PD was dramatically reduced. OVA was chemically stable as OVA-PD-Lipos, when
OVA-PD-Lipos was incorporated into a dissolving microneedle array. Institute of
Cancer Research mice treated with OVA-PD-Lipos-MNs showed a significantly
enhanced immune response. PD combined with OVA elicited a balanced Th1 and Th2
humoral immune response in mice, with minimal irritation in rabbit skin.
Conclusion: The dissolving microneedle array-based system is
a promising delivery vehicle for subunit vaccine and its adjuvant.
Keywords: subunit
vaccine, saponin adjuvant, liposomes, dissolving microneedle array, intradermal
vaccination