109451
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

不同途径注射 (神经周围注射与静脉注射) 地塞米松 (Dexamethasone) 作为局部麻醉辅助剂的比较:一个系统评价和荟萃分析
Authors Zhao WL, Ou XF, Liu J, Zhang WS
Received 28 March 2017
Accepted for publication 2 June 2017
Published 4 July 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1529—1543
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S138212
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr E. Alfonso Romero-Sandoval
Background: Dexamethasone is a common adjuvant for local anesthetics in
regional anesthesia, but the optimal route of administration is controversial.
Therefore, we did a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials to assess the effect of perineural versus intravenous
dexamethasone on local anesthetic regional nerve-blockade outcomes.
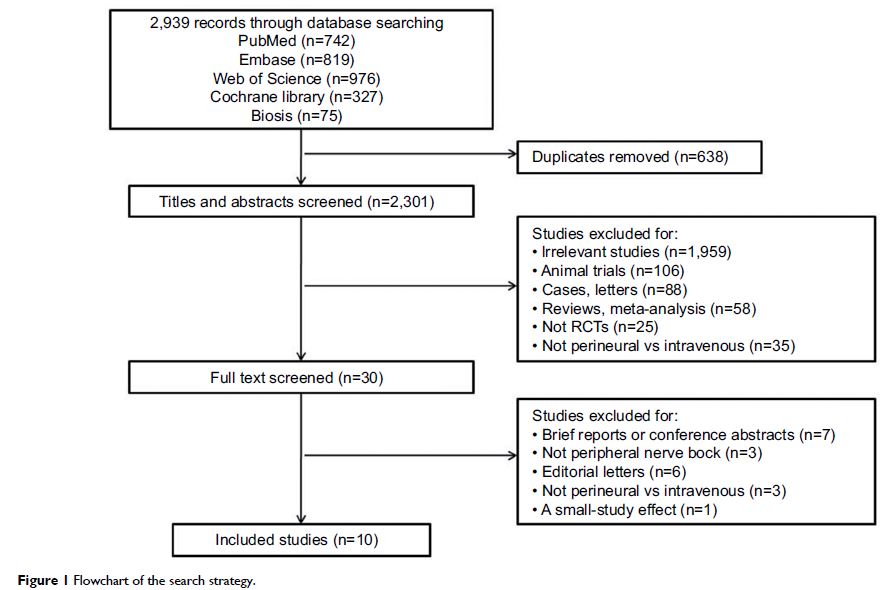
Materials and methods: Medline (through PubMed), Embase, Cochrane, Web
of Science, and Biosis Previews databases were systematically searched
(published from inception of each database to January 1, 2017) to identify
randomized controlled trials. The data of the selected trials were
statistically analyzed to find any significant differences between the two
modalities. The primary outcome was the duration of analgesia. Secondary
outcomes included duration of motor block, postoperative nausea and vomiting,
and postoperative analgesic dose at 24 hours. We conducted a planned subgroup
analysis to compare the effects between adding epinephrine or not.
Results: Ten randomized controlled trials met the
inclusion criteria of our analysis, with a total of 749 patients. Without the
addition of epinephrine, the effects of perineural and intravenous
dexamethasone were equivalent concerning the duration of analgesia (mean
difference 0.03 hours, 95% CI –0.17 to 0.24). However, with the addition of
epinephrine, the analgesic duration of perineural dexamethasone versus
intravenous dexamethasone was prolonged (mean difference 3.96 hours, 95% CI
2.66–5.27). Likewise, the impact of epinephrine was the same on the duration of
motor block. The two routes of administration did not show any significant
differences in the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting, nor on
postoperative analgesic consumption at 24 hours.
Conclusion: Our results show that perineural dexamethasone
can prolong the effects of analgesic duration when compared to the intravenous
route, only when epinephrine is coadministered. Without epinephrine, the two
modalities show equivalent effect as adjuvants on regional anesthesia.
Keywords: anesthesia
adjuvants, dexamethasone, regional anesthesia