109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:加载 siRNA 的聚 (组氨酸 - 精氨酸)6-修饰的壳聚糖纳米颗粒具有强化的细胞穿透和内体逃逸能力,可用于抑制乳腺肿瘤转移
Authors Sun P, Huang W, Kang L, Jin M, Fan B, Jin H, Wang Q, Gao Z
Received 4 December 2016
Accepted for publication 1 February 2017
Published 19 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3221—3234
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S129436
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
***本文章已被撤回***
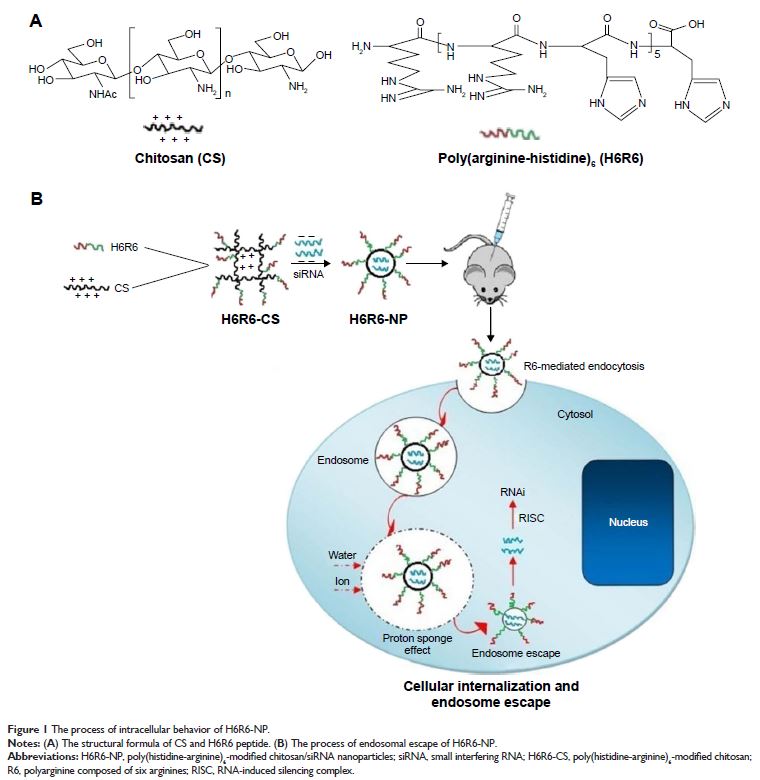
Abstract: An ideal carrier that delivers small interfering RNA (siRNA) should be
designed based on two criteria: cellular-mediated internalization and endosomal
escape. Poly(histidine-arginine)6(H6R6) peptide
was introduced into chitosan (CS) to create a new CS derivative for siRNA
delivery, 6-polyarginine (R6) as cell-penetrating peptides facilitated
nanoparticle cellular internalization has been proved in our previous research,
and 6-polyhistidine (H6) mediated the nanoparticle endosome escape resulted in
the siRNA rapid releasing into tumor cytoplasm. H6R6-modified CS nanoparticles
showed higher transfection efficiency and better endosomal escape capacity
compared to ungroomed CS nanoparticle in vitro. Noticeably, H6R6-modified CS
nanoparticles effectively inhibited tumor cell growth and metastases in vivo
and significantly improved survival ratio. Therefore, we concluded that
H6R6-modified CS copolymer can act as an ideal carrier for siRNA delivery and
as a promising candidate in breast cancer therapy.
Keywords: poly(histidine-arginine)6-peptide-modified chitosan nanoparticle,
cell-penetrating peptides, endosome/lysosome escape, gene delivery, breast
carcinoma