109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

碳纳米管基胶原蛋白水凝胶可改善细胞对准和心脏构造的表现
Authors Sun HY, Zhou J, Huang Z, Qu LL, Lin N, Liang CX, Dai RW, Tang LJ, Tian FZ
Received 17 November 2016
Accepted for publication 14 February 2017
Published 13 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3109—3120
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S128030
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ashutosh Singhal
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
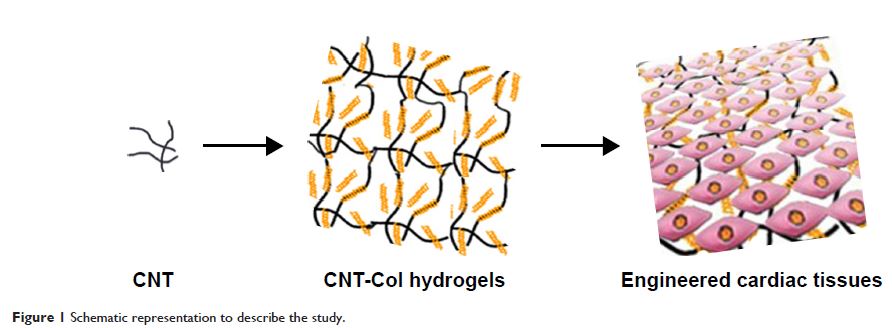
Abstract: Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) provide an essential 2-D microenvironment for
cardiomyocyte growth and function. However, it remains to be elucidated whether
CNT nanostructures can promote cell–cell integrity and facilitate the formation
of functional tissues in 3-D hydrogels. Here, single-walled CNTs were
incorporated into collagen hydrogels to fabricate (CNT/Col) hydrogels, which
improved mechanical and electrical properties. The incorporation of CNTs (up to
1 wt%) exhibited no toxicity to cardiomyocytes and enhanced cell adhesion and
elongation. Through the use of immunohistochemical staining, transmission
electron microscopy, and intracellular calcium-transient measurement, the
incorporation of CNTs was found to improve cell alignment and assembly
remarkably, which led to the formation of engineered cardiac tissues with
stronger contraction potential. Importantly, cardiac tissues based on CNT/Col
hydrogels were noted to have better functionality. Collectively, the
incorporation of CNTs into the Col hydrogels improved cell alignment and the
performance of cardiac constructs. Our study suggests that CNT/Col hydrogels
offer a promising tissue scaffold for cardiac constructs, and might serve as
injectable biomaterials to deliver cell or drug molecules for cardiac
regeneration following myocardial infarction in the near future.
Keywords: carbon nanotubes, collagen hydrogel,
cardiac constructs, cell alignment, tissue functionality