109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利用壳聚糖纳米颗粒进行的 NKG2D-IL-21 融合基因递送抑制小鼠结肠癌的生长
Authors Tan L, Han S, Ding S, Xiao W, Ding Y, Qian L, Wang C, Gong W
Received 17 November 2016
Accepted for publication 28 March 2017
Published 13 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3095—3107
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S128032
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Nanoparticles can be loaded with exogenous DNA for the potential
expression of cytokines with immune-stimulatory function. NKG2D identifies
major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related protein in human and
retinoic acid early induced transcript-1 in mouse, which acts as
tumor-associated antigens. Biologic agents based on interleukin 21 (IL-21) have
displayed antitumor activities through lymphocyte activation. The NKG2D–IL-21
fusion protein theoretically identifies tumor cells through NKG2D moiety and
activates T cells through IL-21 moiety. In this study, double-gene fragments
that encode the extracellular domains of NKG2D and IL-21 genes were connected
and then inserted into the pcDNA3.1(–) plasmid. PcDNA3.1–dsNKG2D–IL-21 plasmid
nanoparticles based on chitosan were generated. Tumor cells pretransfected with
dsNKG2D–IL-21 gene nanoparticles can activate natural killer (NK) and CD8+ T
cells in vitro. Serum IL-21 levels were enhanced in mice intramuscularly
injected with the gene nanoparticles. DsNKG2D–IL-21 gene nanoparticles
accumulated in tumor tissues after being intravenously injected for ~4–24 h.
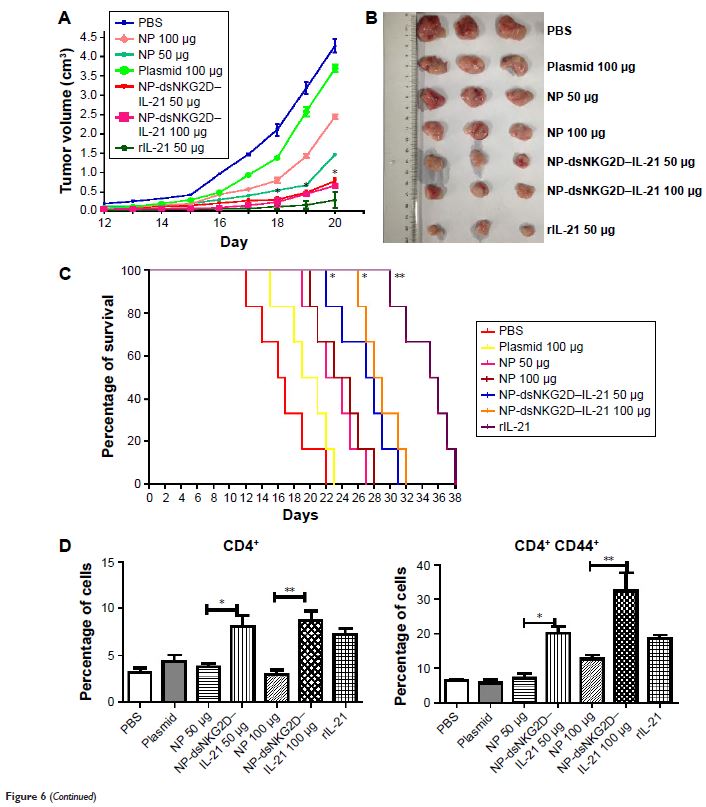
Treatment of dsNKG2D–IL-21 gene nanoparticles also retarded tumor growth and
elongated the life span of tumor-bearing mice by activating NK and T cells
in vivo. Thus, the dsNKG2D–IL-21 gene nanoparticles exerted efficient antitumor
activities and would be potentially used for tumor therapy.
Keywords: NKG2D, IL-21, fusion gene, cancer,
chitosan nanoparticle