109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利奥西呱 (Riociguat):一个用于治疗肺动脉高压的可溶性鸟苷酸 (guanylate) 环化酶刺激剂
Authors Lian TY, Jiang X, Jing ZC
Received 15 July 2016
Accepted for publication 25 December 2016
Published 13 April 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 1195—1207
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S117277
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr James Janetka
Abstract: Despite advances in treatments and improved survival, patients with
pulmonary hypertension still experience poor exercise and functional capacity,
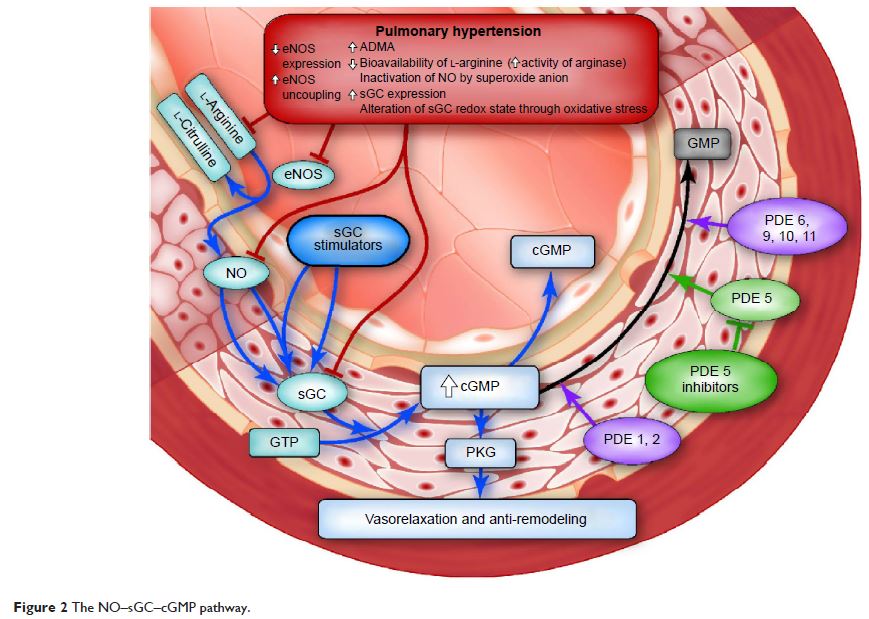
which has a significant detrimental impact on their quality of life. The nitric
oxide (NO)–soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC)–cyclic guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate
(cGMP) pathway has been shown to play an important role in cardiovascular
physiology, especially in vasodilation and pulmonary vascular tone. The oral
sGC stimulator riociguat has a dual mode of action on the NO–sGC–cGMP pathway:
direct stimulation of sGC independent of NO and indirect simulation via
sensitization of sGC to endogenous NO. Riociguat is now licensed in >50
countries worldwide, including in Europe, the USA, Canada, and Japan. Approval
for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) was based on Phase
III data from the PATENT studies, in which riociguat significantly improved
exercise capacity, pulmonary vascular resistance, a range of secondary end
points, and hemodynamic parameters in patients with symptomatic PAH. In the
Phase III CHEST studies, riociguat consistently improved exercise capacity in
patients with inoperable chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH)
or persistent/recurrent CTEPH after pulmonary endarterectomy and is now the
only drug to be approved for this indication. Riociguat was well tolerated in
long-term studies of PAH and CTEPH. This review describes the role of the
NO–sGC–cGMP pathway in the pathophysiology of pulmonary hypertension, and reviews
the clinical efficacy and safety of riociguat in patients with PAH and
inoperable or persistent/recurrent CTEPH. Based on its demonstrated efficacy
and established safety profile, riociguat is a promising treatment option for
patients with PAH and CTEPH.
Keywords: CTEPH, PAH, pulmonary hypertension,
riociguat, sGC stimulator