109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

乳腺癌患者在术后的健康信息认知能力与功能性锻炼的依从性
Authors Tang W, Li Z, Tang C, Wang X, Wang H
Received 16 November 2016
Accepted for publication 23 February 2017
Published 13 April 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 781—786
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S127925
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Naifeng Liu
Purpose: To improve the quality of life of patients who received
modified radical mastectomy, we investigated the factors affecting health
literacy (HL) and exercise adherence in postoperative breast cancer patients
and analyzed the relationship between them.
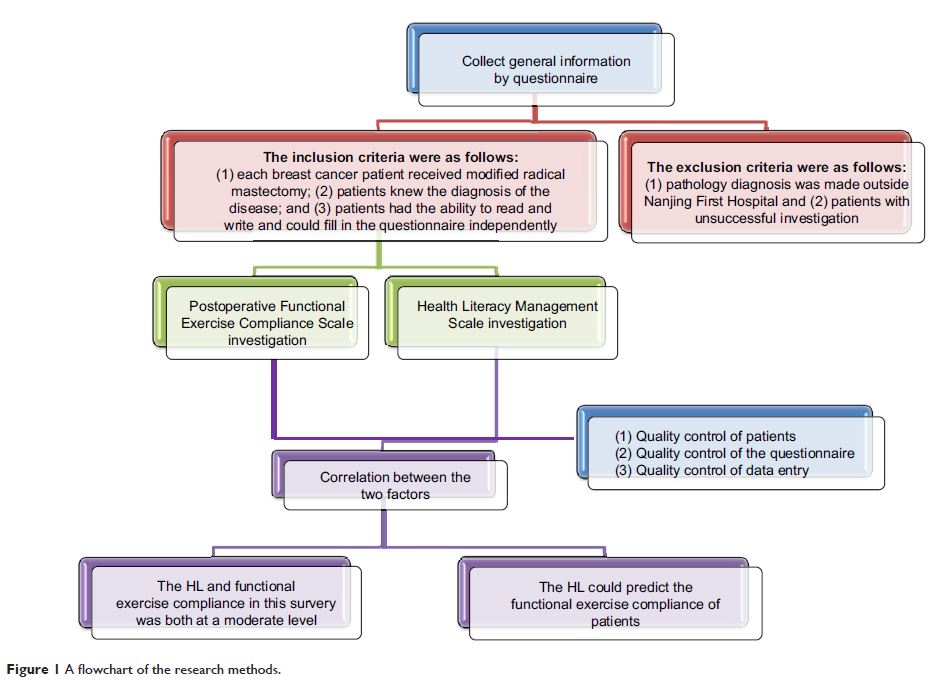
Methods: With random sampling method, we selected patients who
received modified radical mastectomy in Nanjing First Hospital as research
subjects. Then, questionnaires were given to 286 breast cancer patients who met
the inclusion criteria (from January 2014 to June 2016). The questionnaire
includes three parts: General Information, the Health Literacy Scale, and the
Postoperative Functional Exercise Compliance Scale for Breast Cancer Patients.
In this study, the count data were presented as frequency and constituent ratio
and the measurement data were presented as mean ± standard error. Correlation
and logistic analysis were both performed by using SPSS for Windows v.19.0.
Results: This study showed that the total mean score of
postoperative functional exercise compliance of breast cancer patients was
82.65±12.38 points, and the total mean score of postoperative functional
exercise compliance of breast cancer patients was 46.16±3.88 points. In
addition, HL had a strong association with functional exercise compliance in
each dimension except for economic support and proactively seeking advice
compliance.
Conclusion: HL and functional exercise compliance of breast cancer
after radical mastectomy in Nanjing First Hospital were both at a moderate
level and need further improvement. HL could predict the functional exercise
compliance of patients.
Keywords: postoperative,
modified radical mastectomy, patient, health literacy, exercise adherence