109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用 CREKA-共轭的纳米颗粒将胸腺素 β4 靶向递送至损伤的心肌
Authors Huang Z, Song Y, Pang Z, Zhang B, Yang H, Shi H, Chen J, Gong H, Qian J, Ge J
Received 8 January 2017
Accepted for publication 2 March 2017
Published 12 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 3023—3036
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S131949
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
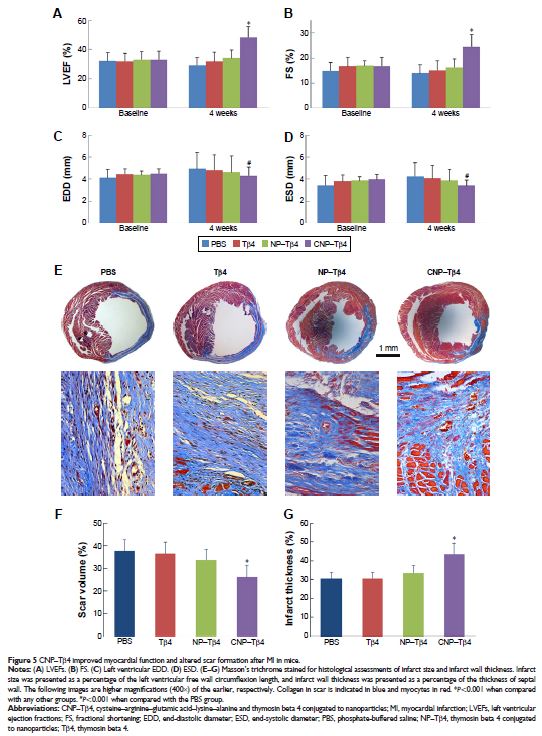
Purpose: Thymosin beta 4 (Tβ4) has multiple beneficial facets for myocardial injury,
but its efficiency is limited by the low local concentration within the
infarct. Here, we established a Tβ4 delivery system for cardiac repair based on
the interaction between the abundant fibrin in the infarct zone and the
fibrin-targeting moiety clot-binding peptide cysteine–arginine–glutamic
acid–lysine–alanine (CREKA).
Methods and results: CREKA and Tβ4 were conjugated to
nanoparticles (CNP–Tβ4). In vitro binding test revealed that CNP–Tβ4 had a
significant binding ability to the surface of fibrin clots when compared to the
control clots (NP–Tβ4). Based on the validation of fibrin expression in the
early stage of ischemia injury, CNP–Tβ4 was intravenously administered to mice
with acute myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. CNP–Tβ4 revealed a stronger
fibrin-targeting ability than the NP–Tβ4 group and accumulated mainly in the
infarcted area and colocalized with fibrin. Subsequently, treatment with
CNP–Tβ4 resulted in a better therapeutic effect.
Conclusion: CRKEA modification favored Tβ4 accumulation and
retention in the infarcted region, leading to augmented functional benefits.
Fibrin-targeting delivery system represents a generalizable platform technology
for regenerative medicine.
Keywords: thymosin beta 4, fibrin, CREKA,
targeting delivery, ischemia reperfusion, cardiovascular