109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

由 TiO2 纳米管及 GL13K 抗微生物肽组成的植入物涂层的抗菌活性和细胞相容性
Authors Li T, Wang N, Chen S, Lu R, Li H, Zhang Z
Received 26 November 2016
Accepted for publication 11 February 2017
Published 12 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2995—3007
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S128775
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Prevention of implant-associated infections at an early stage of surgery
is highly desirable for the long-term efficacy of implants in dentistry and
orthopedics. Infection prophylaxis using conventional antibiotics is becoming
less effective due to the development of bacteria resistant to multiple
antibiotics. An ideal strategy to conquer bacterial infections is the local
delivery of antibacterial agents. Therefore, antimicrobial peptide (AMP)
eluting coatings on implant surfaces is a promising alternative. In this study,
the feasibility of utilizing TiO2 nanotubes (TNTs), processed using
anodization, as carriers to deliver a candidate AMP on titanium surfaces for
the prevention of implant-associated infections is assessed. The broad-spectrum
GL13K (GKIIKLKASLKLL-CONH2) AMP derived from human parotid secretory protein
was selected and immobilized to TNTs using a simple soaking technique. Field
emission scanning electron microscope, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared
spectroscopy, and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analyses confirmed
the successful immobilization of GL13K to anatase TNTs. The drug-loaded
coatings demonstrated a sustained and slow drug release profile in vitro and
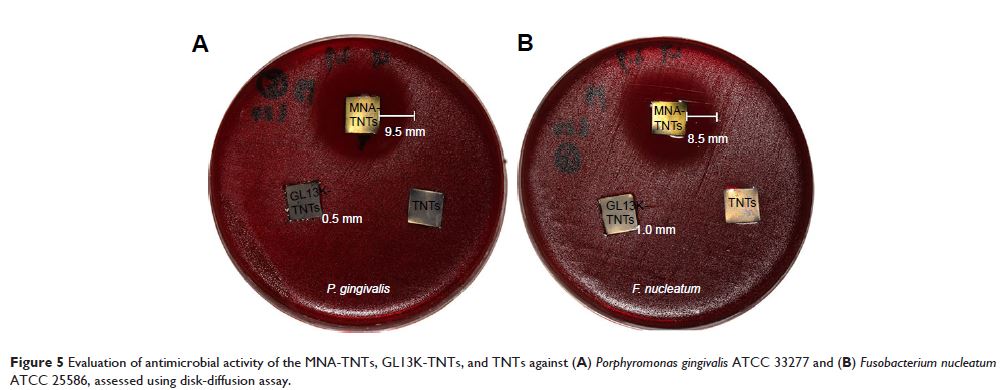
eradicated the growth of Fusobacterium nucleatum and Porphyromonas gingivalis within 5 days of culture, as assessed
by disk-diffusion assay. The GL13K-immobilized TNT (GL13K-TNT) coating
demonstrated greater biocompatibility, compared with a coating produced by
incubating TNTs with equimolar concentrations of metronidazole. GL13K-TNTs
produced no observable cytotoxicity to preosteoblastic cells (MC3T3-E1). The
coating may also have an immune regulatory effect, in support of rapid
osseointegration around implants. Therefore, the combination of TNTs and AMP
GL13K may achieve simultaneous antimicrobial and osteoconductive activities.
Keywords: orthopedic infections, titanium,
nanotubes, antimicrobial peptide