109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CUL4A 通过激活 NF-κB 信号通路促进胃癌细胞侵袭
Authors Gong Y, Xiang XJ, Feng M, Chen J, Fang Z, Xiong J
Received 30 November 2016
Accepted for publication 18 January 2017
Published 12 April 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 45—53
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/BTT.S127650
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Doris Benbrook
Abstract: Cullin 4A (CUL4A ) overexpression has been
reported to be involved in the carcinogenesis and progression of many malignant
tumors. However, the role of CUL4A in the progression of gastric cancer
(GC) remains unclear. In this study, we explored whether and how CUL4A regulates proinflammatory signaling to
promote GC cell invasion. Our results showed that knockdown of CUL4A inhibited GC cell migration and
invasion induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. We also found that
both CUL4A and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) protein expressions were enhanced
by LPS stimulation in HGC27 GC cell lines. Furthermore, knockdown of CUL4A decreased the protein expression of
NF-κB and mRNA expression of the downstream genes of the NF-κB pathway, such as
matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 2, MMP9, and interleukin-8. Our
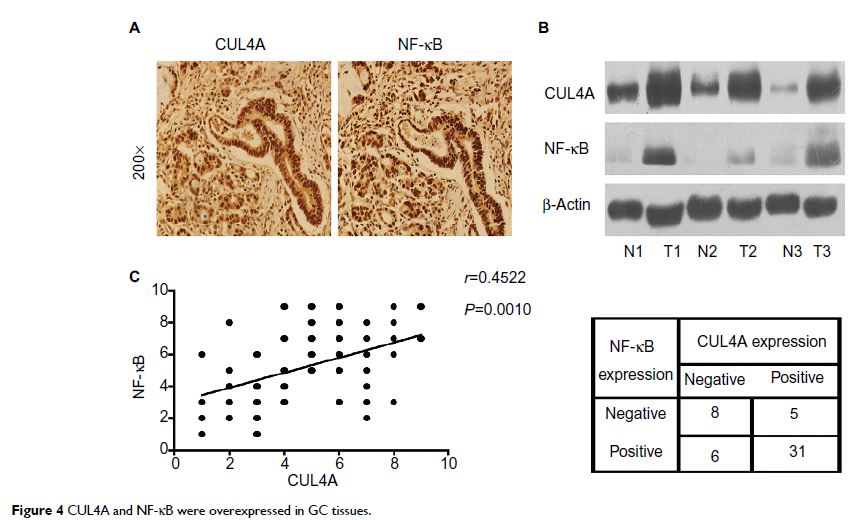
immunohistochemistry analysis on 50 GC tissue samples also revealed that CUL4A
positively correlated with NF-κB expression. Taken together, our findings
suggest that CUL4A may promote GC cell invasion by
regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway and could be considered as a potential
therapeutic target in patients with GC.
Keywords: CUL4A , NF-κB, gastric cancer,
invasion