109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

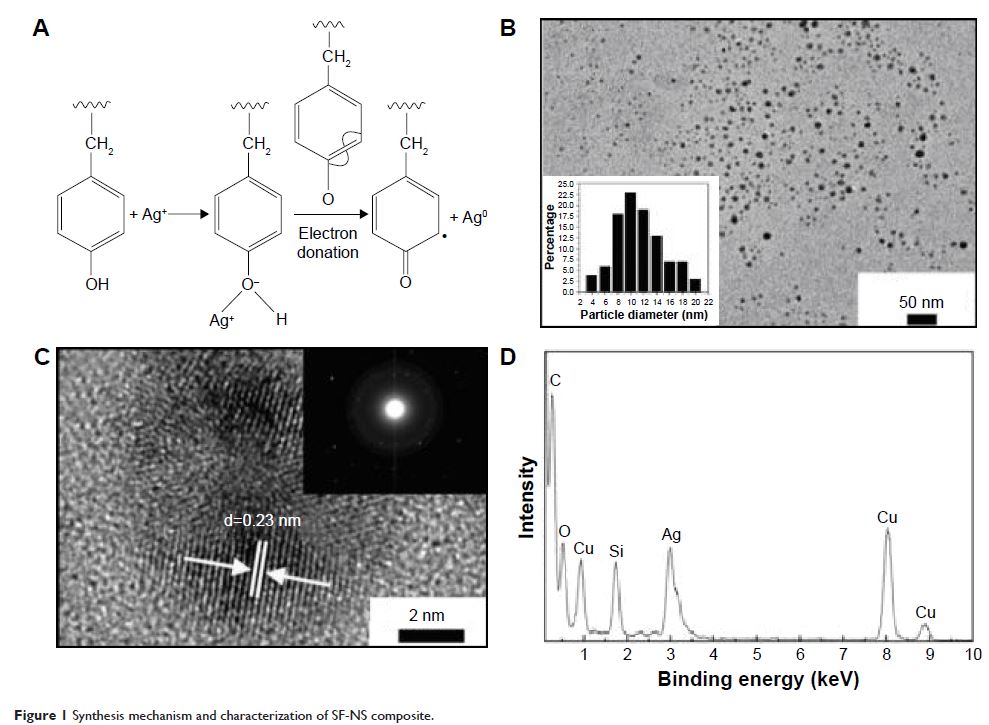
丝素蛋白纳米银对金黄色葡萄球菌 (Staphylococcus aureus ) 及生物膜相关鼻窦炎兔模型的疗效
Authors Jia M, Chen Z, Guo Y, Chen X, Zhao X
Received 13 December 2016
Accepted for publication 20 March 2017
Published 10 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2933—2939
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S130160
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Staphylococcus
aureus biofilms contribute significantly to the
recalcitrant nature of chronic rhinosinusitis. In previous studies, it has been
shown that silk fibroin–nano silver solution can eliminate S. aureus biofilms in vitro, which suggests a
potential role of this novel agent in the treatment of biofilm-associated
diseases, such as sinusitis.
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy
of silk fibroin–nano silver solution as a topical anti-biofilm agent in a
rabbit model of sinusitis.
Methods: Biofilm-associated sinusitis models were established
in 24 New Zealand White rabbits by gelatin sponge placement and S. aureus inoculation through a hole drilled
into the anterolateral wall of the right maxillary sinus. After 4 weeks,
indwelling catheters were placed into the maxillary sinus. Different
concentrations of silk fibroin–nano silver solution or normal saline were
irrigated slowly into the maxillary sinus via the indwelling catheters. After 7
days of irrigation, the rabbits were sacrificed. The sinus mucosa was harvested
and examined for biofilm biomass as well as morphological integrity of the
epithelium by scanning electron microscopy.
Results: Silk fibroin–nano silver solution was found to be most
effective in reducing the biomass of the S. aureus biofilms at a concentration of 384
mg/L, followed by the concentration of 153.6 mg/L, when compared with saline.
After treatment with 384 mg/L silk fibroin–nano silver solution, the biofilms
were completely eliminated and the injured epithelium was almost restored with
regenerated cilia on the surface.
Conclusion: Silk fibroin–nano silver solution was found to be an
effective topical agent against S. aureus biofilms in the rabbit model of
sinusitis, and its effect was concentration-dependent.
Keywords: chronic rhinosinusitis, nasal
irrigation, maxillary sinus, biomass, scanning electron microscopy, animal