109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

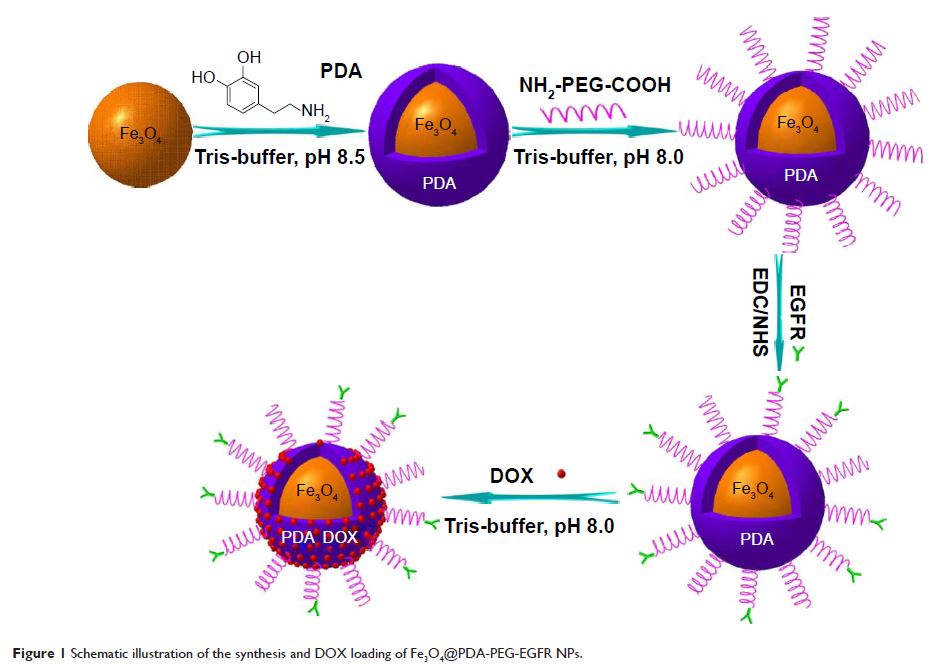
负载 DOX 的 Fe3O4@ 聚多巴胺多功能纳米复合材料用于 MRI 和抗肿瘤化学光热治疗
Authors Mu X, Zhang F, Kong C, Zhang H, Zhang W, Ge R, Liu Y, Jiang J
Received 31 December 2016
Accepted for publication 1 March 2017
Published 10 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2899—2911
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S131418
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jiang Yang
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Multifunctional nanocomposites that have multiple therapeutic functions
together with real-time imaging capabilities have attracted intensive concerns
in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. This study developed epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) antibody-directed polydopamine-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Fe3O4@PDA NPs) for
magnetic resonance imaging and antitumor chemo-photothermal therapy. The
synthesized Fe3O4@PDA-PEG-EGFR-DOX
NPs revealed high storage capacity for doxorubicin (DOX) and high photothermal
conversion efficiency. The cell viability assay of Fe3O4@PDA-PEG-EGFR NPs
indicated that Fe3O4@PDA-PEG-EGFR NPs
had no cell cytotoxicity. However, Fe3O4@PDA-PEG-EGFR-DOX NPs could significantly decrease
cell viability (~5% of remaining cell viability) because of both photothermal
ablation and near-infrared light-triggered DOX release. Meanwhile, the
EGFR-targeted Fe3O4@PDA-PEG-EGFR-DOX
NPs significantly inhibited the growth of tumors, showing a prominent
in vivo synergistic antitumor effect. This study demonstrated the
potential of using Fe3O4@PDA NPs for
combined cancer chemo-photothermal therapy with increased efficacy.
Keywords: Fe3O4 nanoparticles,
polydopamine, chemo-photothermal therapy, multifunctional nanocomposites, DOX