109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

在黄芩素 (Baicalein) 口服递送中使用基于大麻油的生物相容性纳米乳液和较少的表面活性剂,可增强生物利用度
Authors Yin J, Xiang C, Wang P, Yin Y, Hou Y
Received 27 December 2016
Accepted for publication 1 March 2017
Published 10 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2923—2931
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S131167
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Jiang Yang
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
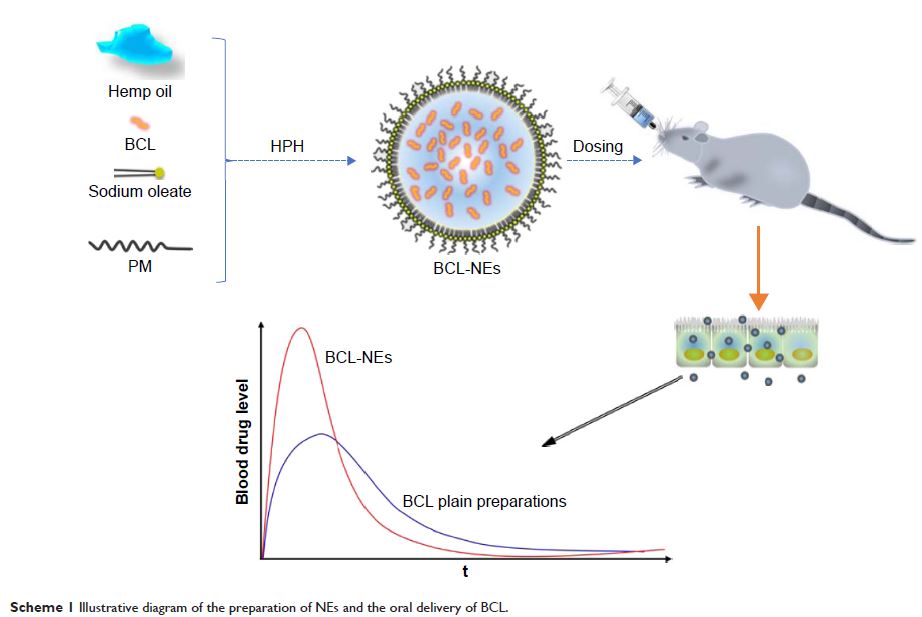
Abstract: Baicalein (BCL) possesses high pharmacological activities but low
solubility and stability in the intestinal tract. This study aimed to probe the
potential of nanoemulsions (NEs) consisting of hemp oil and less surfactants in
ameliorating the oral bioavailability of BCL. BCL-loaded NEs (BCL-NEs) were
prepared by high-pressure homogenization technique to reduce the amount of
surfactants. BCL-NEs were characterized by particle size, entrapment efficiency
(EE), in vitro drug release, and morphology. Bioavailability was studied in
Sprague-Dawley rats following oral administration of BCL suspensions, BCL
conventional emulsions, and BCL-NEs. The obtained NEs were ~90 nm in
particle size with an EE of 99.31%. BCL-NEs significantly enhanced the oral
bioavailability of BCL, up to 524.7% and 242.1% relative to the suspensions and
conventional emulsions, respectively. BCL-NEs exhibited excellent intestinal
permeability and transcellular transport ability. The cytotoxicity of BCL-NEs
was documented to be low and acceptable for oral purpose. Our findings suggest
that such novel NEs and preparative process provide a promising alternative to
current formulation technologies and suitable for oral delivery of drugs with
bioavailability issues.
Keywords: baicalein, nanoemulsions, biocompatibility,
high-pressure homogenization, hemp oil, bioavailability