109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过脂质乳剂对不混溶的亲水/疏水化学治疗剂进行有效的共同递送,以改善癌症治疗
Authors Zhang B, Song YM, Wang TQ, Yang SM, Zhang J, Liu YJ, Zhang N, Garg S
Received 30 November 2016
Accepted for publication 24 February 2017
Published 7 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2871—2886
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S129091
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Combinational nanomedicine is becoming a topic of much interest in
cancer therapy, although its translation into the clinic remains extremely
challenging. One of the main obstacles lies in the difficulty to efficiently
co-deliver immiscible hydrophilic/hydrophobic drugs into tumor sites. The aim
of this study was to develop co-loaded lipid emulsions (LEs) to co-deliver
immiscible hydrophilic/hydrophobic drugs to improve cancer therapy and to
explore the co-delivery abilities between co-loaded LEs and mixture
formulation. Multiple oxaliplatin/irinotecan drug–phospholipid complexes (DPCs)
were formulated. Co-loaded LEs were prepared using DPC technique to efficiently
encapsulate both drugs. Co-loaded LEs exhibited uniform particle size
distribution, desired stability and synchronous release profiles in both drugs.
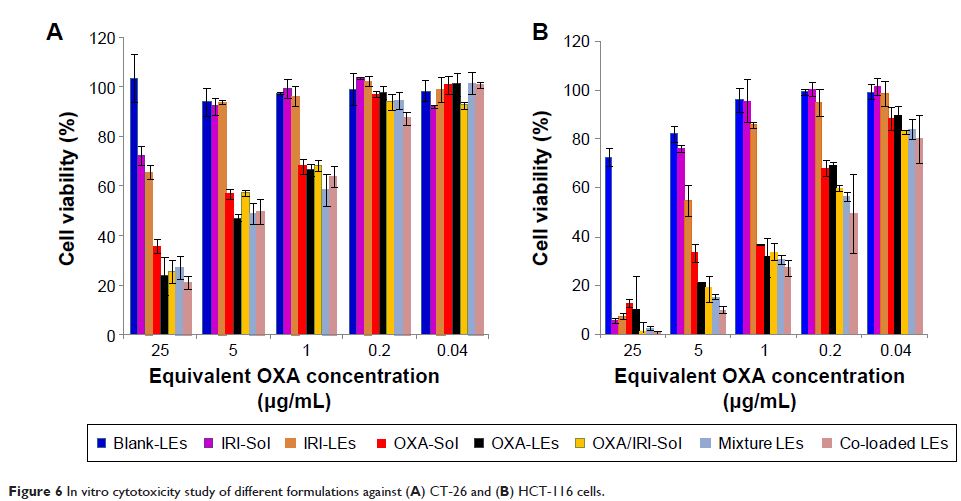
Co-loaded LEs demonstrated superior anti-tumor activity compared with the
simple solution mixture and the mixture of single-loaded LEs. Furthermore,
co-loaded nanocarriers could co-deliver both drugs into the same cells more
efficiently and exhibited the optimized synergistic effect. These results
indicate that co-loaded LEs could be a desired formulation for enhanced cancer
therapy with potential application prospects. The comparison between co-loaded
LEs and mixture formulation is significant for pharmaceutical designs aimed at
co-delivery of multiple drugs.
Keywords: cancer, combination therapy,
co-delivery, lipid emulsions, drug–phospholipid complex