109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA NBAT-1 抑制肿瘤发生并预测卵巢癌的预后良好
Authors Yan CS, Jiang Y, Wan YC, Zhang L, Liu JH, Zhou SL, Cheng WJ
Received 14 October 2016
Accepted for publication 3 December 2016
Published 6 April 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1993—2002
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S124645
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Samir Farghaly
Abstract: Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) has been proven to be involved in many biological
processes in ovarian cancer (OC). However, the mechanism still remains unknown.
In this study, we screened significantly downregulated NBAT-1, which has been
proven to play a significant role in breast cancer, clear cell renal cell
carcinoma, and neuroblastoma, but not in OC, in two independent datasets with
relatively more samples (GSE18520 and GSE38666) from Gene Expression Omnibus.
We found that lncRNA NBAT-1 was obviously downregulated in OC tissue compared
to normal ovarian tissue (P <0.001) which
was free of OC, and the detected levels of NBAT-1 were associated with the
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage and tumor size
guidelines. Moreover, it has been shown that lower levels of NBAT-1 predict
poor outcomes of OC. In order to investigate the functional role of NBAT-1,
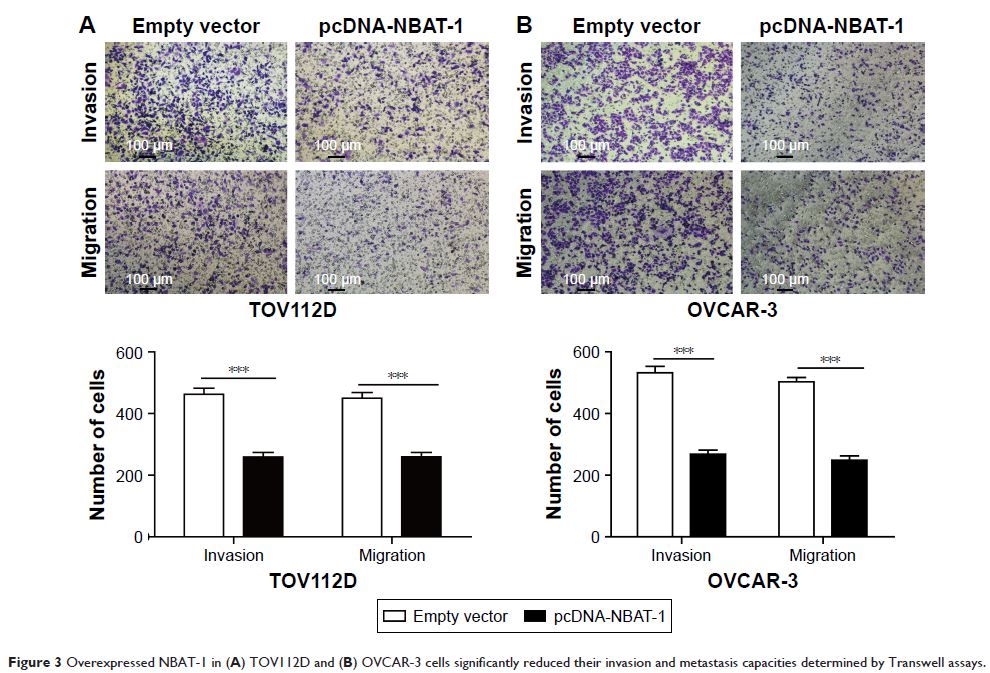
pcDNA-NBAT-1 and empty vector were transfected into TOV112D and OVCAR-3 cell
lines. Overexpressed NBAT-1 significantly inhibited cell proliferation,
invasion, and migration in both TOV112D and OVCAR-3 cell lines. Finally,
Western blot assay indicated that NBAT-1 may exert its function by targeting
the ERK1/2 and AKT signaling pathways. In addition, tumor formation growth
assay showed that overexpressed NBAT-1 significantly suppresses tumor growth in
vivo. In conclusion, our study suggests that NBAT-1 acts as an anti-oncogene in
the development of OC.
Keywords: ovarian cancer, lncRNA NBAT-1,
tumorigenesis, prognosis