109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

精氨酸 (Arginine) - 甘氨酸 (glycine) - 天冬氨酸 (aspartic) - 肽共轭的量子点所诱导的光动力疗法对胰腺癌的体内效应
Authors Li MM, Cao J, Yang JC, Shen YJ, Cai XL, Chen YW, Qu CY, Zhang Y, Shen F, Xu LM
Received 21 December 2016
Accepted for publication 16 March 2017
Published 5 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2769—2779
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S130799
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Alexander Kharlamov
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Abstract: Quantum dots (QDs) conjugated with integrin antagonist
arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (RGD) peptides (QDs-RGD) are novel nanomaterials
with a unique optical property: a high molar extinction coefficient.
Previously, we have shown that QDs-RGD demonstrate a photodynamic therapy (PDT)
effect as new photosensitizers for the pancreatic cancer cell line SW1990 in
vitro. Here, we investigate the application of QDs-RGD in mice bearing
pancreatic tumors using PDT. To ensure that more photosensitizers accumulated
in tumors, QDs-RGD were injected intratumorally. After selection of an adequate
dosage for injection from analyses of biodistribution images captured by an
IVIS system, PDT was initiated. Three groups were created according to
different PDT procedures. In group 1, mice were injected with QDs-RGD
intratumorally, and an optical fiber connected to a laser light was inserted
directly into the tumor. Irradiation was sustained for 20 min with a laser
light (630 nm) at 100 mW/cm2. In group 2, the
laser optical fiber was placed around, and not inserted into, tumors. In group
3, PDT was conducted as in group 1 but without injection of QDs-RGD. After
28 days of observation, tumors on the back of mice in group 1 grew slowly
(V/V0 =3.24±0.70) compared with the control groups, whose
tumors grew quickly, and the mean V/V0 reached 6.08±0.50
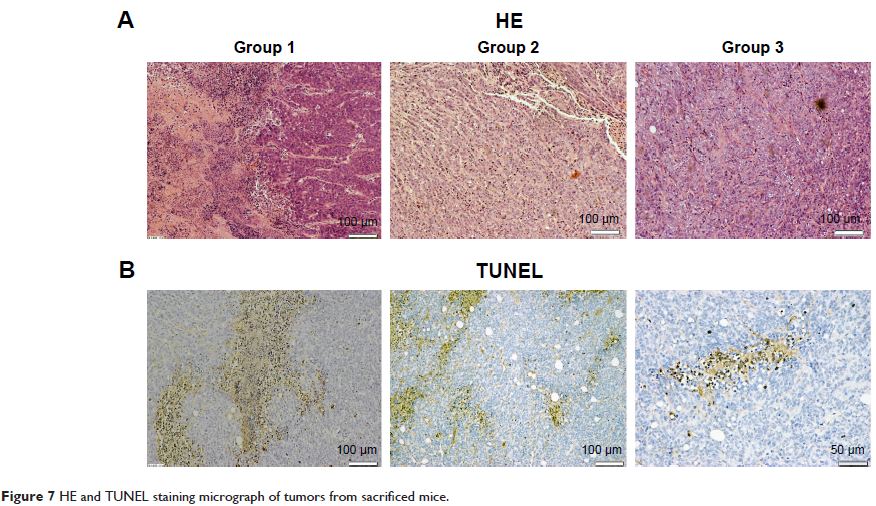
(group 2) and 7.25±0.82 (group 3). Histology of tumor tissues showed more
necrotic tissues, more inflammatory cells, and less vascular tissue in the PDT
group than those in the control groups. These results suggest that
QDs-RGD-mediated PDT, with illumination using an optical fiber inserted
directly into the tumor, can inhibit the growth of SW1990 tumors with high
efficiency in nude mice.
Keywords: quantum dots, RGD peptides, pancreatic
neoplasm, intratumoral injection, photodynamic therapy