109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

多孔羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖和白蛋白/壳聚糖支架对颅盖缺损骨再生作用的比较研究
Authors Zhou D, Qi C, Chen Y, Zhu YJ, Sun T, Chen F, Zhang C
Received 29 December 2016
Accepted for publication 4 March 2017
Published 4 April 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2673—2687
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S131251
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Akshita Wason
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Hydroxyapatite (HAP; Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2) and whitlockite (WH; Ca18Mg2(HPO4)2(PO4)12) are widely
utilized in bone repair because they are the main components of hard tissues
such as bones and teeth. In this paper, we synthesized HAP and WH hollow
microspheres by using creatine phosphate disodium salt as an organic phosphorus
source in aqueous solution through microwave-assisted hydrothermal method.
Then, we prepared HAP/chitosan and WH/chitosan composite membranes to evaluate
their biocompatibility in vitro and prepared porous HAP/chitosan and
WH/chitosan scaffolds by freeze drying to compare their effects on bone
regeneration in calvarial defects in a rat model. The experimental results
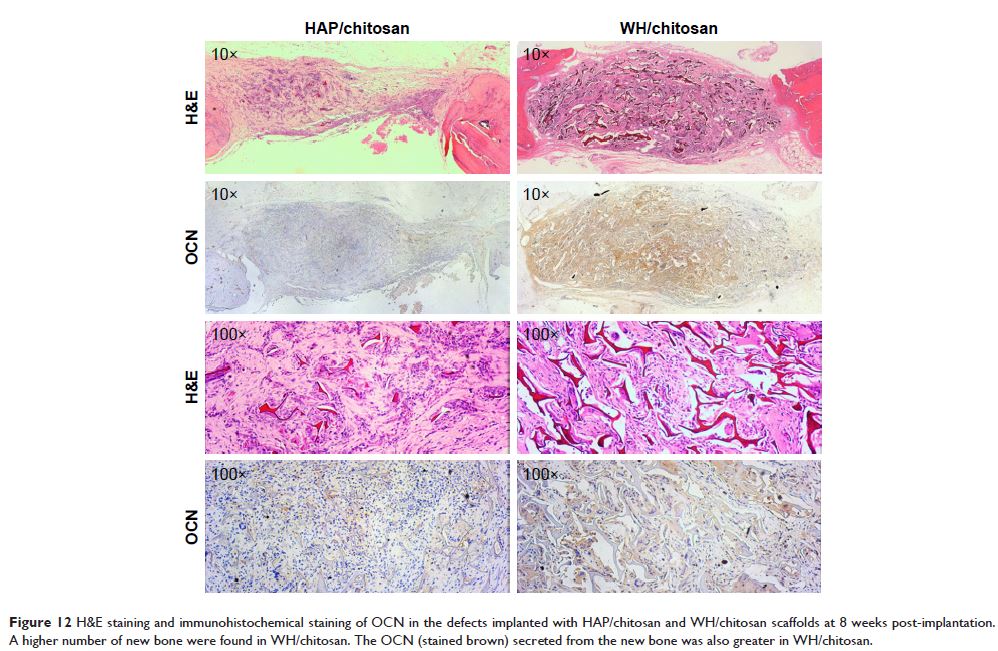
indicated that the WH/chitosan composite membrane had a better
biocompatibility, enhancing proliferation and osteogenic differentiation
ability of human mesenchymal stem cells than HAP/chitosan. Moreover, the porous
WH/chitosan scaffold can significantly promote bone regeneration in calvarial
defects, and thus it is more promising for applications in tissue engineering
such as calvarial repair compared to porous HAP/chitosan scaffold.
Keywords: hydroxyapatite, whitlockite, chitosan,
osteogenic differentiation, rat critical calvarial defect, tissue engineering