109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

催眠敏感性较高或较低的参与者的催眠与个性特征之间的关系
Authors Zhang Y, Wang Y, Shen C, Ye Y, Shen S, Zhang B, Wang J, Chen W, Wang W
Received 17 February 2017
Accepted for publication 7 March 2017
Published 3 April 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 1007—1012
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S134930
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Papan Thaipisuttikul
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wai Kwong Tang
Background: The relationship between normal personality and hypnotic susceptibility
is important for understanding mental processing and mental disorders, but it
is less consistent in normal people or in patients with a psychiatric disorder.
We have hypothesized that the correlation exists but varies in individuals with
different levels of hypnotizability.
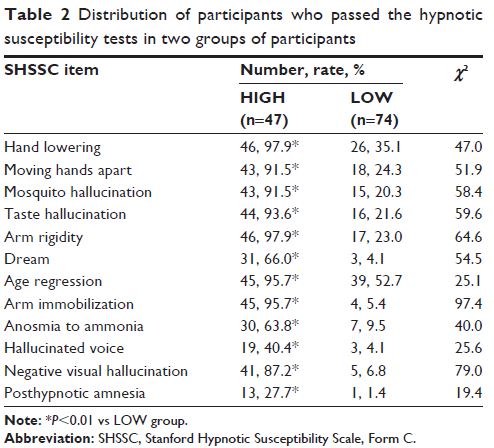
Participants and methods: We invited 72 individuals with high (HIGH group) and
47 individuals with low (LOW group) hypnotic susceptibilities to undertake
tests of NEO-PI-R and the Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scale, Form C
(SHSSC).
Results: The HIGH group scored significantly higher than the
LOW group did on openness to experience and its facet openness to feelings. In
the LOW group, SHSSC total was positively predicted by openness to ideas; age
regression was positively predicted by openness to experience and negatively
predicted by extraversion; anosmia to ammonia was negatively predicted by
agreeableness; and negative visual hallucination was positively predicted by
openness to experience. In the HIGH group, hallucinated voice was positively
predicted by openness to experience and negatively predicted by agreeableness,
and posthypnotic amnesia was positively predicted by extraversion and
negatively predicted by openness to experience.
Conclusion: The associations between normal personality traits and
hypnotic susceptibility items were weak and different in the two groups, which
imply that managing mental or somatoform disorders might be through adjusting
hypnotizability and mobilizing personality functions.
Keywords: hypnotic susceptibility, NEO-PI-R,
normal personality trait, the Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scale, Form C