9 7 3 1 6
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.3 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.4 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.5 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.5 Clin Interv Aging
- 4.7 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 2.7 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.5 Int J Women's Health
- 2.5 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.7 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.3 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 2.8 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 2.8 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.0 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.7 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.2 J Inflamm Res
- 2.1 Int J Gen Med
- 4.2 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.7 J Asthma Allergy
- 1.9 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.7 J Multidiscip Healthc

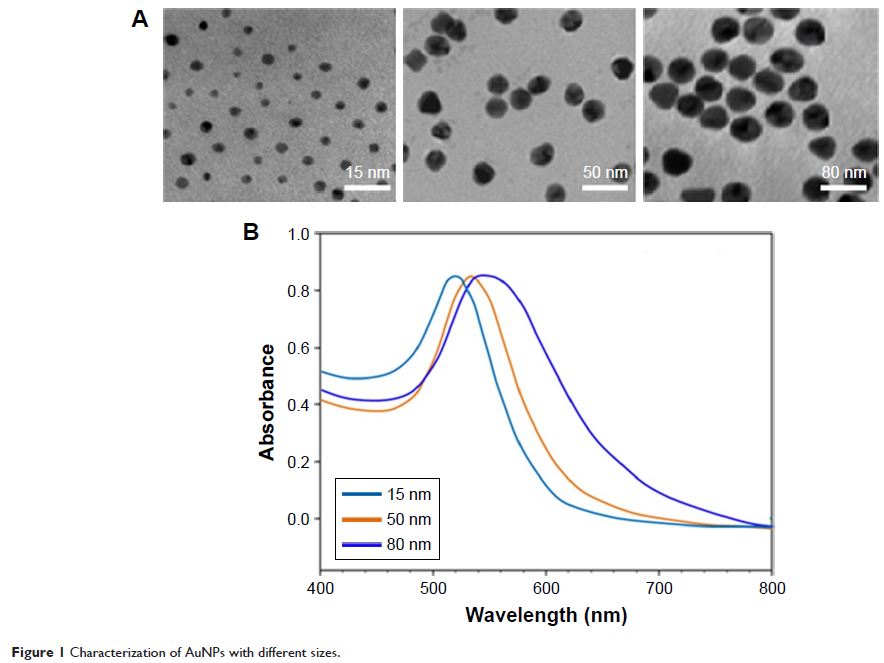
金纳米颗粒通过 Drp1 介导的细胞凋亡和 NSCLC 细胞中自噬性线粒体裂变提高 TRAIL 敏感性
Authors Ke S, Zhou T, Yang P, Wang Y, Zhang P, Chen K, Ren L, Ye S
Received 2 December 2016
Accepted for publication 28 February 2017
Published 31 March 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2531—2551
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S129274
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Thiruganesh Ramasamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: Although tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)
and its agonistic receptors have been identified as highly promising antitumor
agents preferentially eliminating cancer cells with minimal damage, the
emergence of TRAIL resistance in most cancers may contribute to therapeutic
failure. Thus, there is an urgent need for new approaches to overcome TRAIL
resistance. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are one of the most promising
nanomaterials that show immense antitumor potential via targeting various
cellular and molecular processes; however, the effects of AuNPs on TRAIL
sensitivity in cancer cells remain unclear. In this study, we found that AuNPs
combined with TRAIL exhibited a greater potency in promoting apoptosis in
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells compared with TRAIL alone, suggesting
that AuNPs sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL. Further experiments demonstrated
that the combination of TRAIL and AuNPs was more effective in causing excessive
mitochondrial fragmentation in cancer cells accompanied by a dramatic increase
in mitochondrial recruitment of dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1), mitochondrial
dysfunctions, and enhancement of autophagy induction. Small interfering RNA
(siRNA) silencing of Drp1 or inhibition of autophagy could effectively
alleviate apoptosis in cells exposed to TRAIL combined with AuNPs. In vivo
studies revealed that AuNPs augmented TRAIL sensitivity in tumor-bearing mice.
Our data indicated that AuNPs potentiate apoptotic response to TRAIL in NSCLC
cells through Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission, and TRAIL combined with
AuNPs can be a potential chemotherapeutic strategy for the treatment of NSCLC.
Keywords: AuNPs,
TRAIL, mitochondrial dynamics, Drp1, autophagy/mitophagy