109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

耐用抗菌剂和 UV 保护的 Ag/TiO2@ 织物用于可持续的生物医学应用
Authors Li SH, Zhu TX, Huang JY, Guo QQ, Chen GQ, Lai YK
Received 9 January 2017
Accepted for publication 1 March 2017
Published 31 March 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2593—2606
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S132035
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Professor Farooq Shiekh
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
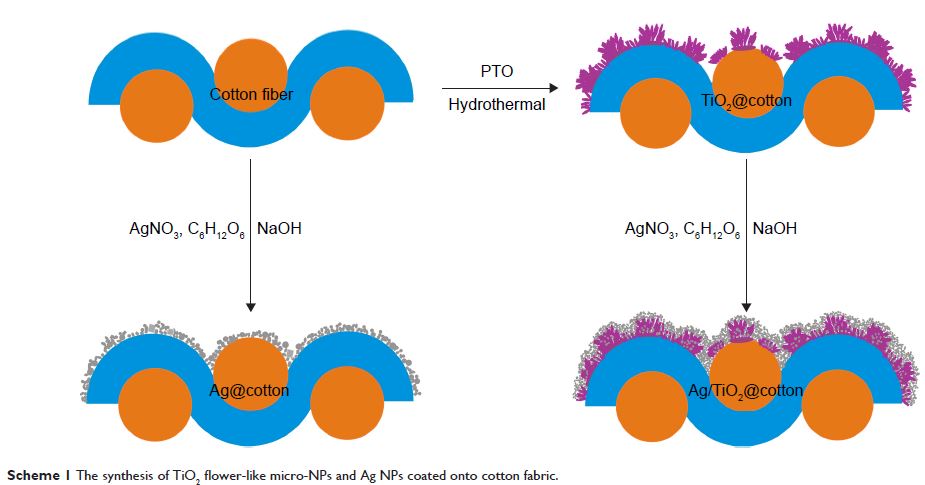
Abstract: A facile method was developed to endow cotton fabric with remarkable
antibacterial and ultraviolet (UV)-protective properties. The flower-like TiO2 micro-nanoparticles
were first deposited onto cotton fabric surface via hydrothermal deposition
method. Then, the Ag NPs with a high deposition density were evenly formed onto
TiO2@cotton surface by sodium hydroxide solution
pretreatment and followed by in situ reduction of ANO3. This work focused on the influence of different
hydrothermal reaction durations and the concentration of AgNO3 on
antibacterial activity against relevant microorganisms in medicine as well as
on the UV-blocking property. Ag NPs-loaded TiO2@cotton exhibited
high antibacterial activity with an inhibition rate higher than 99% against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli bacteria.
Moreover, the as-prepared cotton fabric coated with Ag NPs and TiO2 NPs
demonstrated outstanding UV protective ability with a high ultraviolet
protection factor value of 56.39. Morphological image of the cells revealed a
likely loss of viability as a result of the synergistically biocidal effects of
TiO2 and
Ag on attached bacteria. These results demonstrate a facile and robust synthesis
technology for fabricating multifunctional textiles with a promising biocidal
activity against common Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
Keywords: TiO2 nanoparticles, Ag nanoparticles,
fabric, antibacterial, UV-shielding, biomedical