109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
对比 UGIB 的预防效果,以及 PPIs 与 H2RAs (联合 DAPT) 对血小板功能影响: 一个系统评价和综合分析
Authors Yi Z, Qiu T, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Zhai S
Received 10 November 2016
Accepted for publication 3 March 2017
Published 24 March 2017 Volume 2017:13 Pages 367—377
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S127292
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Hoa Le
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Deyun Wang
Objective: We compared
prophylactic effects of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and histamine-2 receptor
antagonists (H2RAs) on upper gastrointestinal
bleeding (UGIB) associated with dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) and explored
this influence on platelet function.
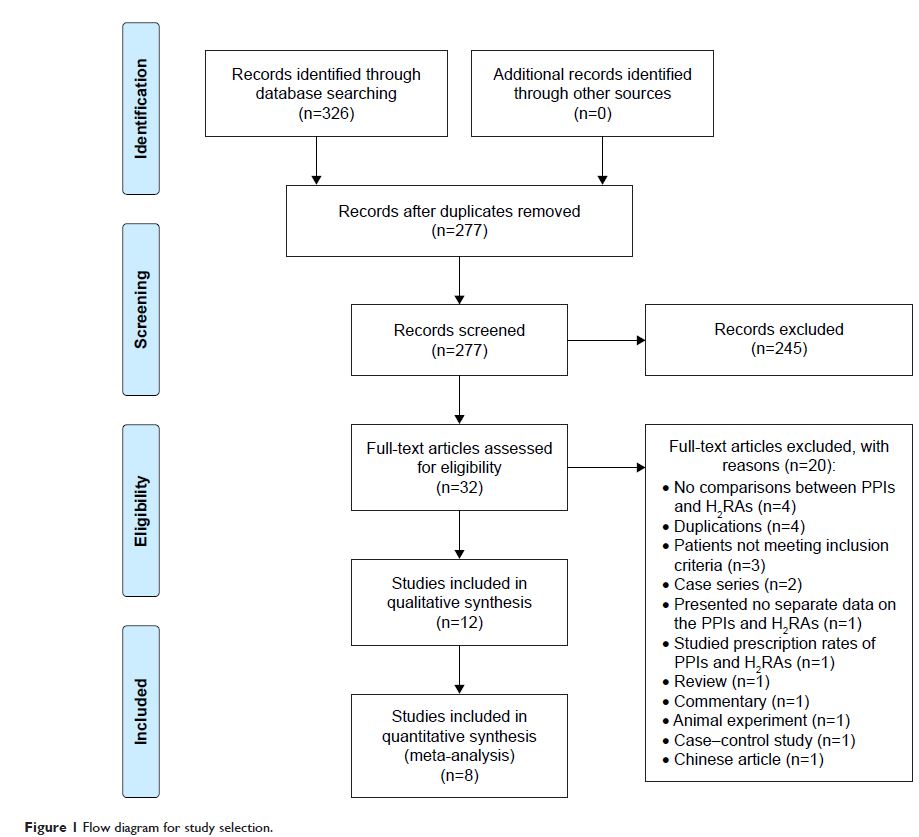
Methods: Randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing PPIs with H2RAs in adults receiving DAPT were collected from PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane databases. Dichotomous data were pooled to obtain risk ratios (RRs) for UGIB, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), poor responders to clopidogrel and rehospitalization, and continuous data were pooled to obtain mean differences (MDs) for P2Y12 reaction units (PRUs), with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: Twelve clinical trials (n=3,301) met the inclusion criteria. Compared to H2RAs, PPIs lessened UGIB (RR =0.16, 95% CI: 0.03–0.70), and there was no significant difference in the incidence of PRUs (MD =18.21 PRUs, 95% CI: -4.11–40.54), poor responders to clopidogrel (RR =1.21, 95% CI: 0.92–1.61), incidence of MACEs (RR =0.89, 95% CI: 0.45–1.75) or rehospitalization (RR =1.76, 95% CI: 0.79–3.92). Subgroup analysis confirmed fewer PRUs in the H2RAs group compared to the omeprazole group (2 studies, n=189, MD =31.80 PRUs, 95% CI: 11.65–51.96). However, poor responder data for clopidogrel and MACEs might be unreliable because few studies of this kind were included.
Conclusion: Limited evidence indicates that PPIs were better than H2RAs for prophylaxis of UGIB associated with DAPT and had no effect on platelet function. Further study is needed to confirm these observations.
Keywords: proton pump inhibitors, histamine-2 receptor antagonists, dual-antiplatelet therapy, upper gastrointestinal bleeding, platelet function, meta-analysis
Methods: Randomized controlled trials and cohort studies comparing PPIs with H2RAs in adults receiving DAPT were collected from PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane databases. Dichotomous data were pooled to obtain risk ratios (RRs) for UGIB, major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs), poor responders to clopidogrel and rehospitalization, and continuous data were pooled to obtain mean differences (MDs) for P2Y12 reaction units (PRUs), with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: Twelve clinical trials (n=3,301) met the inclusion criteria. Compared to H2RAs, PPIs lessened UGIB (RR =0.16, 95% CI: 0.03–0.70), and there was no significant difference in the incidence of PRUs (MD =18.21 PRUs, 95% CI: -4.11–40.54), poor responders to clopidogrel (RR =1.21, 95% CI: 0.92–1.61), incidence of MACEs (RR =0.89, 95% CI: 0.45–1.75) or rehospitalization (RR =1.76, 95% CI: 0.79–3.92). Subgroup analysis confirmed fewer PRUs in the H2RAs group compared to the omeprazole group (2 studies, n=189, MD =31.80 PRUs, 95% CI: 11.65–51.96). However, poor responder data for clopidogrel and MACEs might be unreliable because few studies of this kind were included.
Conclusion: Limited evidence indicates that PPIs were better than H2RAs for prophylaxis of UGIB associated with DAPT and had no effect on platelet function. Further study is needed to confirm these observations.
Keywords: proton pump inhibitors, histamine-2 receptor antagonists, dual-antiplatelet therapy, upper gastrointestinal bleeding, platelet function, meta-analysis