109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

抗 RhoC siRNA 通过调节 KAI1,MMP9 和 CXCR4 的表达来抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖和侵袭
Authors Xu X, Shen H, Zhu L, Lu J, Zhang L, Luo Z, Wu Y
Received 27 July 2015
Accepted for publication 22 June 2016
Published 23 March 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1827—1834
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S93164
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Professor Da Li
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Faris Farassati
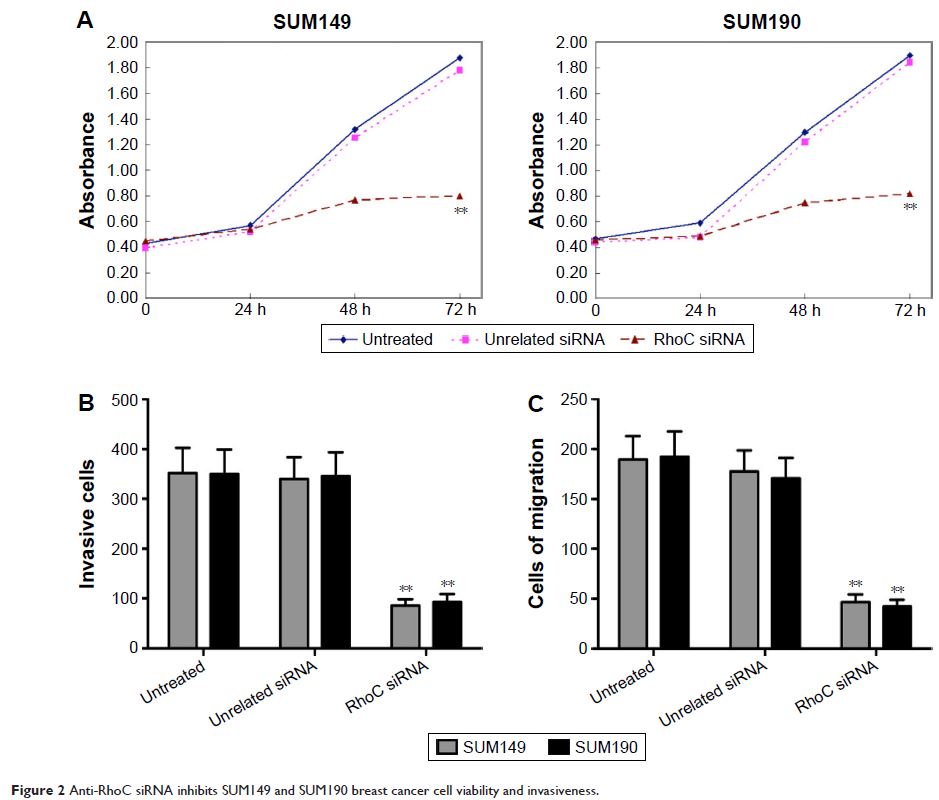
Abstract: Overexpression of RhoC in breast cancer cells indicates poor prognosis.
In the present study, we aim to investigate the possible antitumor effects of
anti-RhoC small-interfering RNA (siRNA) in inflammatory breast cancer cells. In
this study, a specific anti-RhoC siRNA was used to inhibit RhoC synthesis.
Transfection of anti-RhoC siRNA into two IBC cells SUM149 and SUM190 induced
extensive degradation of target mRNA and led to significant decrease in the
synthesis of protein. Anti-RhoC siRNA inhibited cell proliferation and
invasion, increased cell apoptosis, and induced cell cycle arrest in vitro.
Moreover, the transfection of siRNA increased the expression of KAI1 and decreased
the expression of MMP9 and CXCR4 in both mRNA and protein levels. Furthermore,
transplantation tumor experiments in BALB/c-nu mice showed that intratumoral
injection of anti-RhoC siRNA inhibited tumor growth and increased survival
rate. Our results suggested that RhoC gene silencing with specific anti-RhoC
siRNA would be a potential therapeutic method for metastatic breast cancer.
Keywords: gene silencing, proliferation,
apoptosis, cell cycle arrest