109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

抗菌肽 DP7 与抗生素相结合产生抗多重耐药性细菌的协同作用
Authors Wu X, Li Z, Li X, Tian Y, Fan Y, Yu C, Zhou B, Liu Y, Xiang R, Yang L
Received 25 February 2016
Accepted for publication 7 April 2016
Published 22 March 2017 Volume 2017:11 Pages 939—946
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S107195
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Ranjeet Sinha
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Professor Wei Duan
Abstract: Antibiotic-resistant bacteria present a great
threat to public health. In this study, the synergistic effects of
antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and antibiotics on several multidrug-resistant
bacterial strains were studied, and their synergistic effects on azithromycin
(AZT)-resistance genes were analyzed to determine the relationships between
antimicrobial resistance and these synergistic effects. A checkerboard method
was used to evaluate the synergistic effects of AMPs (DP7 and CLS001) and
several antibiotics (gentamicin, vancomycin [VAN], AZT, and amoxicillin) on
clinical bacterial strains (Staphylococcus aureus , Pseudomonas aeruginosa , Acinetobacter baumannii ,
and Escherichia coli ). The AZT-resistance genes (ermA , ermB , ermC , mefA , and msrA ) were
identified in the resistant strains using quantitative polymerase chain
reaction. For all the clinical isolates tested that were resistant to different
antibiotics, DP7 had high antimicrobial activity (≤32 mg/L). When DP7 was
combined with VAN or AZT, the effect was most frequently synergistic. When we
studied the resistance genes of the AZT-resistant isolates, the synergistic
effect of DP7–AZT occurred most frequently in highly resistant strains or
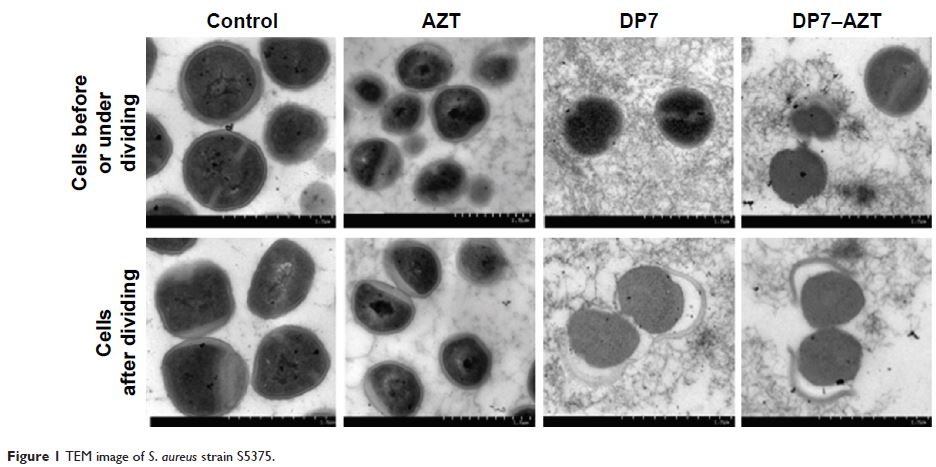
strains carrying more than two AZT-resistance genes. A transmission electron
microscopic analysis of the S. aureus strain
synergistically affected by DP7–AZT showed no noteworthy morphological changes,
suggesting that a molecular-level mechanism plays an important role in the
synergistic action of DP7–AZT. AMP DP7 plus the antibiotic AZT or VAN is more
effective, especially against highly antibiotic-resistant strains.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptide, drug synergy,
resistant bacteria