109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

Efficacy and safety of guaifenesin for upper back, neck, and shoulder pain: a Phase II proof-of-concept, multicenter, placebo-controlled, repeat-dose, parallel-group study
Authors Collaku A, Yue Y, Reed K
Received 1 November 2016
Accepted for publication 26 January 2017
Published 21 March 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 669—678
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S126296
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Schatman
Background/objective: Guaifenesin, an over-the-counter (OTC) expectorant, has exhibited muscle
relaxant effects preclinically and clinically. This proof-of-principle study
explored whether OTC doses of guaifenesin can provide relief from acute upper
back, neck, or shoulder muscle spasm and pain.
Methods: This multicenter, placebo-controlled, repeat-dose, parallel study randomly
assigned adults experiencing acute pain and muscle spasm in their upper back,
neck, or shoulder to guaifenesin 600 or 1200 mg or matched placebo twice
daily (BID) in a 2:2:1:1 ratio for 7 days. The primary end point was the
change from baseline in muscle spasm relief, measured using an 11-point numeric
rating scale (0= not present to 10= unbearable) recorded twice daily and
averaged over the 7-day treatment period. Analyses were performed using a
linear mixed model that included treatment as a fixed effect and site as a
random effect.
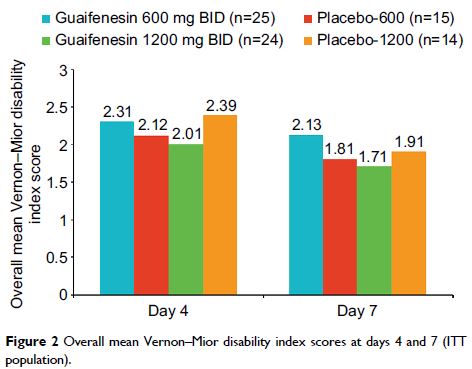
Results: A total of 77 subjects were included in the 4 treatment groups. Least
squares mean muscle spasm score over 7 days was 1.77 with guaifenesin
1200 mg, 1.42 with its matched placebo, 1.53 with guaifenesin 600 mg,
and 1.74 with its matched placebo. Treatment with guaifenesin 1200 mg BID
provided 25% greater reduction in mean muscle spasm over its matched placebo
and 16% greater reduction than guaifenesin 600 mg BID. These differences
were not statistically significant. Based on comparisons of absolute mean
values, a consistent directional change in effect was observed, suggesting some
benefit from placebo to lower-to-upper doses of guaifenesin with regard to
muscle spasm, tension, pain, discomfort, and relaxation. No severe or serious
adverse events were reported.
Conclusion: Results suggest the potential for OTC dose of guaifenesin 1200 mg
BID to provide symptomatic relief of upper back musculoskeletal pain and spasm.
Confirmation of this preliminary result in a larger, adequately powered study
is needed.
Keywords: guaifenesin, upper back pain, muscle spasm, muscle relaxation,
Vernon–Mior disability assessment