109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

The association of weight loss with patient experience and outcomes in a population of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus prescribed canagliflozin
Authors Gerlanc NM, Cai J, Tkacz J, Bolge SC, Brady BL
Received 9 December 2016
Accepted for publication 17 January 2017
Published 20 March 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 89—99
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S129824
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Ming-Hui Zou
Objective: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic condition complicated by
being overweight or obese. This study used a patient survey to assess health,
satisfaction, and diabetes self-management in relation to weight management.
Methods: A survey including the Current Health Satisfaction
Questionnaire, Diabetes Distress Scale, and Diabetes Treatment Satisfaction
Questionnaire was administered using an online platform to a sample of 205
patients with T2DM prescribed canagliflozin. Patients were placed into 5 groups
based on their self-reported weight change since initiation of canagliflozin:
Lost >10 lbs, Lost 5–10 lbs, Lost <5 lbs, No Change, and Gained Weight.
One-way ANOVAs, Kruskall–Wallis tests, and multivariable regression were used
to explore differences between weight loss groups.
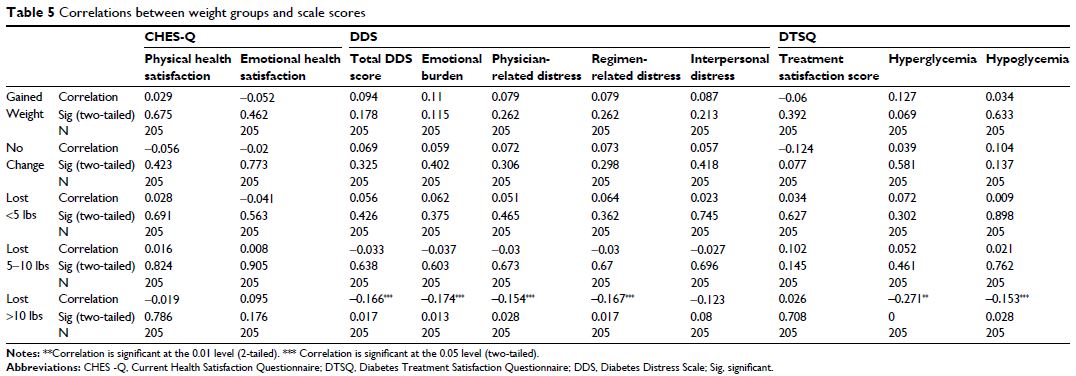
Results: The majority of patients (66.8%) reported losing
weight. Compared to other groups, patients who lost >10 lbs were more likely
to be engaged in a weight loss program for at least 6 months. Patients in the
Lost >10 lbs and Lost 5–10 lbs groups reported the greatest satisfaction
with canagliflozin (p <0.05 for
both). Multivariable analyses controlling for patient demographic and treatment
characteristics revealed that losing >10 lbs was associated with reduced
diabetes distress, improved A1c and blood glucose levels, and decreased
perceived frequency of hyperglycemia (p <0.05).
Conclusion: Increased positive patient outcomes, engagement in
diabetes self-management, and medication satisfaction were observed among
patients who reported weight loss. These findings suggest that a T2DM regimen
that includes canagliflozin as part of a weight loss regimen can help improve
patient outcomes and experiences with T2DM.
Keywords: T2DM, patient outcomes, diabetes self-management,
SGLT2 inhibitor, weight management