109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

利伐沙班 (Rivaroxaban) 对中国血管病变患者的治疗应用
Authors Chen W, Fan L, Wang Y, Deng XH
Received 29 January 2017
Accepted for publication 21 February 2017
Published 17 March 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 621—624
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S133462
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Katherine Hanlon
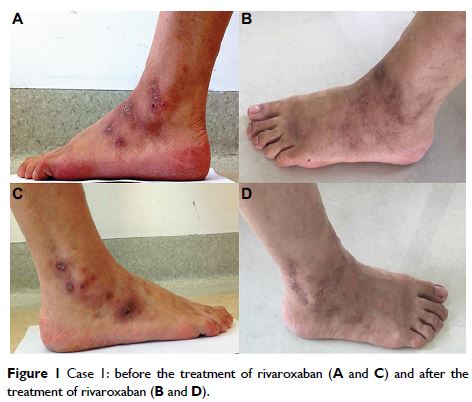
Abstract: Livedoid vasculopathy (LV) is a chronic prothrombotic disease of
cutaneous microcirculation resulting in cutaneous ischemia and infarction. As a
rare disease, LV has an estimated incidence of ten cases per million. Not only
correct diagnosis but also effective treatments are very difficult for patients
with LV. Due to the lack of large-scale studies in this rare disease, LV poses
a great challenge to the doctors, and existing treatment has always been an
individual attempt with off-label application. The main goals in the treatment
of patients with LV are to avoid the repeated occurrence of active cutaneous
lesions and prevent painful ulceration and irreversible scarring. The current
report describes the cases of three Chinese patients with LV receiving rivaroxaban
treatment, an oral direct inhibitor of factor Xa inhibitor, and observes the
treatment effect of rivaroxaban during the follow-up. As an injection-free
alternative to low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWP) and monitoring-free
alternative to warfarin, rivaroxaban improves the quality of life and enhances
the compliance of patients. All patients consider rivaroxaban as more tolerable
than previous drugs and, therefore, continue the application of rivaroxaban,
effectively improving the treatment effect of drugs and successfully avoiding
the repeated occurrence of active cutaneous lesions. Treatment application of
rivaroxaban in Chinese patients with LV successfully avoids the recurrence of
active cutaneous lesions and prevents the progressive ulceration and scarring.
Keywords: livedoid vasculopathy, rivaroxaban