109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血管收缩-2-共轭聚乙二醇-聚-ε-己内酯共聚物聚合酶用于双重靶向药物递送至大鼠神经胶质瘤
Authors Lu F, Pang Z, Zhao J, Jin K, Li H, Pang Q, Zhang L, Pang Z
Received 28 September 2016
Accepted for publication 27 December 2016
Published 16 March 2017 Volume 2017:12 Pages 2117—2127
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S123422
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lakshmi Kiran Chelluri
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Abstract: The blood–brain barrier is a formidable obstacle for glioma chemotherapy
due to its compact structure and drug efflux ability. In this study, a
dual-targeting drug delivery system involving Angiopep-2-conjugated
biodegradable polymersomes loaded with doxorubicin (Ang-PS-DOX) was developed
to exploit transport by the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1
(LRP1), which is overexpressed in both blood–brain barrier and glioma cells.
The polymersomes (PS) were prepared using a thin-film hydration method. The PS
were loaded with doxorubicin using the pH gradient method (Ang-PS-DOX). The
resulting PS were uniformly spherical, with diameters of ~135 nm and with
~159.9 Angiopep-2 molecules on the surface of each PS. The drug-loading
capacity and the encapsulation efficiency for doxorubicin were 7.94%±0.17% and
95.0%±1.6%, respectively. Permeability tests demonstrated that the proton
diffusion coefficient across the PS membrane was far slower than that across
the liposome membrane, and the common logarithm value was linearly dependent on
the dioxane content in the external phase. Compared with PS-DOX, Ang-PS-DOX
demonstrated significantly higher cellular uptake and stronger cytotoxicity in
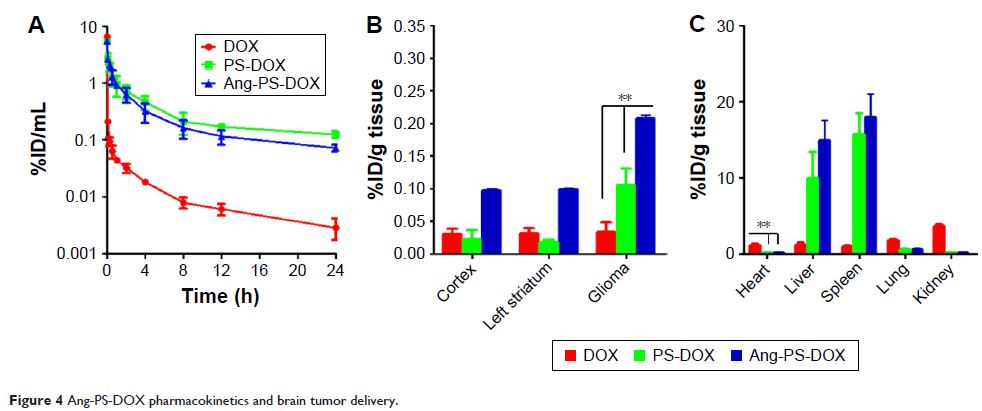
C6 cells. In vivo pharmacokinetics and brain distribution experiments revealed
that Ang-PS-DOX achieved a more extensive distribution and more abundant
accumulation in glioma cells than PS-DOX. Moreover, the survival time of
glioma-bearing rats treated with Ang-PS-DOX was significantly prolonged
compared with those treated with PS-DOX or a solution of free doxorubicin.
These results suggested that Ang-PS-DOX can target glioma cells and enhance
chemotherapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: Angiopep-2, dual targeting,
biodegradable polymersomes, doxorubicin, glioma treatment