109568
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使用磁共振扩散加权成像评估经导管动脉化疗栓塞术对肝细胞癌的疗效
Authors Wu X, Wang J, Ji J, Chen M, Song J
Received 22 June 2016
Accepted for publication 23 November 2016
Published 16 March 2017 Volume 2017:10 Pages 1637—1643
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S115568
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Lucy Goodman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Abstract: Although the efficacy of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE)
has been recommended as first-line therapy for nonsurgical patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), it is difficult to accurately predict the
efficacy of TACE. Therefore, this study evaluated the efficacy of TACE for HCC
using magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). A total of 84
HCC patients who received initial TACE were selected and assigned to the stable
group (n=39) and the progressive group (n=45). Before TACE treatment, a
contrast-enhanced MR scan and DWI (b =300, 600, and 800
s/mm2) were performed on all patients. The modified
response evaluation criteria in solid tumors were used for evaluation of tumor
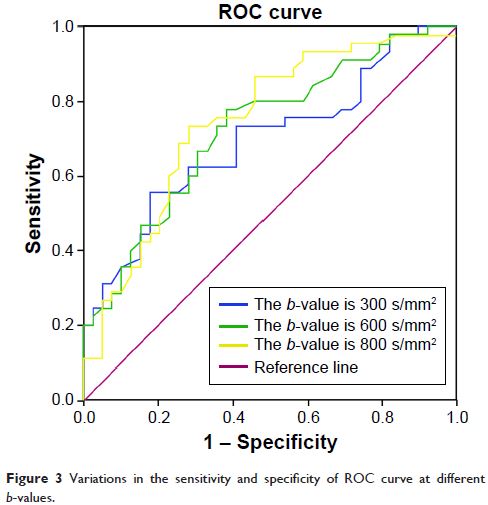
response. Receiver operating characteristic curve was employed to predict the
value of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) for TACE efficacy. The ADC values
of HCC patients in the progressive group were higher than those in the stable
group at different b -values (b =300, 600, and 800 s/mm2) before TACE treatment. The area under the curve of
ADC values with b -values of 300, 600, and 800 s/mm2 were
0.693, 0.724, and 0.746; the threshold values were 1.94×10-3 mm2/s, 1.28×10-3 mm2/s, and 1.20×10-3 mm2/s; the sensitivity values were 55.6%, 77.8%, and
73.3%; and the specificity values were 82.1%, 61.5%, and 71.8%, respectively.
Our findings indicate that the ADC values of MR-DWI may accurately predict the
efficacy of TACE in the treatment of HCC patients.
Keywords: magnetic resonance imaging,
diffusion-weighted imaging, hepatocellular carcinoma, transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization, apparent diffusion coefficient